True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Blood enters the heart through the atria.
|
|
|
2.
|
The only veins that carry oxygen-rich blood are the venae cavae.
|
|
|
3.
|
The blood in the veins is prevented from flowing backward because of valves in
these blood vessels.
|
|
|
4.
|
Red blood cells are produced in the spleen.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
5.
|
Which type of muscle makes up the heart?
a. | cardiac | c. | skeletal | b. | smooth | d. | all of these |
|
|
|
6.
|
A(n) _____ muscle contracts under conscious control.
a. | voluntary | c. | skeletal | b. | involuntary | d. | striated |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which type of muscle moves bones?
a. | skeletal | c. | smooth | b. | striated | d. | voluntary |
|
|
|
8.
|
The skin regulates the temperature of the body on a hot day by _____.
a. | closing the pores | c. | constricting the blood | b. | dilating blood
vessels | d. | reducing access to
the exterior |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which hormone causes an increase in blood glucose?
a. | glycogen | c. | glucagon | b. | gastrin | d. | sucrase |
|
|
|
10.
|
The hormone that causes a decrease in blood glucose is _____.
a. | glucagon | c. | gastrin | b. | insulin | d. | nuclease |
|
|
|
11.
|
The esphagus moves food through a series of involuntary muscular contractions
called _____.
a. | mechanical digestion | c. | peristalsis | b. | chemical digestion | d. | stimuli |
|
|
|
12.
|
What controls the release of food from the stomach to the small
intestine?
a. | villus | c. | epiglottis | b. | larynx | d. | muscular
valve(sphincter) |
|
|
|
13.
|
The first section of the small intestine is called the _____.
a. | appendix | c. | duodenum | b. | rectum | d. | villus |
|
|
|
14.
|
As a result of digestion, proteins are broken down to _____.
a. | monosaccharides | c. | triglycerides | b. | amino acids | d. | glycerol |
|
|
|
15.
|
The body's preferred energy source is _____.
a. | carbohydrates | c. | proteins | b. | fats | d. | minerals |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the most abundant substance in the body?
a. | fat | c. | sugar | b. | water | d. | protein |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following occurs in the large intestine?
a. | absorption of water | b. | synthesis of vitamin K and some B
vitamins | c. | moves indigestible matter to rectum | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following is part of the digestive tract?
a. | liver | c. | gallbladder | b. | stomach | d. | pancreas |
|
|
|
19.
|
The surface area of the small intestine is greatly increased by _____.
a. | a large number of villi | c. | peristalsis | b. | chemical
digestion | d. | mechanical
digestion |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following is not mechanical digestion?
a. | chewing food | c. | churning of the stomach | b. | contractions in
small intestine | d. | action of
pepsin on proteins |
|
|
|
21.
|
Starches are large _____.
a. | fats | c. | complex carbohydrates | b. | proteins | d. | simple
carbohydrates |
|
|
|
22.
|
____ is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus that stimulates the reabsorption
of water in the kidney .
a. | Aldosterone | c. | Antidiuretic hormone(ADH) | b. | Insulin | d. | Glucagon |
|
|
|
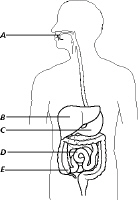 Figure
35-1
|
|
|
23.
|
In Figure 35-1, where is water absorbed?
|
|
|
24.
|
In Figure 35-1, where does protein digestion first take place?
|
|
|
25.
|
In Figure 35-1, which part has the lowest pH?
|
|
|
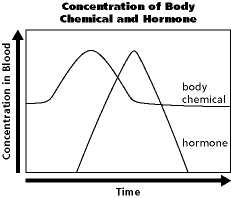 Figure
35-3
|
|
|
26.
|
What type of system is shown in Figure 35-3?
a. | reverse feedback | c. | negative feedback | b. | positive feedback | d. | anti feedback |
|
|
|
27.
|
What is likely to have triggered hormone production shown in Figure 35-3?
a. | the presence of the body chemical | c. | a total lack of the body
chemical | b. | a decrease in the body chemical | d. | an increase in the body
chemical |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which organ filters blood that has collected wastes from cells throughout the
body and maintains the homeostasis of body fluids?
a. | kidneys | c. | lungs | b. | heart | d. | pacemaker |
|
|
|
29.
|
Which of the following expells urine from the body?
a. | urinary bladder | c. | kidneys | b. | urethra | d. | ureters |
|
|
|
30.
|
Which of the following is true of breathing?
a. | homeostatic process | c. | coordinated process | b. | involuntary process | d. | all of these |
|
|
|
31.
|
The filtering unit of the kidney is the ____.
a. | bladder | c. | nephron | b. | ureter | d. | urethra |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following is a function of the kidney?
a. | remove wastes from the blood | c. | adjust the salt level of the
blood | b. | adjust the fluid level of the blood | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
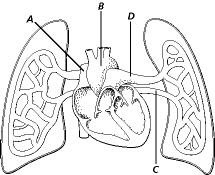 Figure
37-5
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the destination of blood at D in Figure 37-5?
a. | the heart | c. | the body | b. | kidneys | d. | the left lung |
|
|
|
34.
|
How is the blood located in the artery at D in Figure 37-5 different than the
blood in all other arteriess of the body?
a. | it is rich with oxygen | c. | it doesn’t reach the lung | b. | it is rich with
carbon dioxide | d. | it
doesn’t reach the heart |
|
|
|
35.
|
Why is blood pumped through D before B in Figure 37-5?
a. | to enrich it with oxygen | c. | to enrich it with water
| b. | to enrich it with carbon dioxide | d. | to enrich it with blood
cells |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | small intestine | h. | epiglottis | b. | liver | i. | esophagus | c. | bile | j. | target
tissue | d. | thyroid gland | k. | pepsin | e. | amylase | l. | peristalsis | f. | stomach | m. | Calorie | g. | endocrine gland | n. | rectum |
|
|
|
36.
|
Organ that produces bile
|
|
|
37.
|
Ductless organ that releases hormones into the bloodstream
|
|
|
38.
|
Narrow, muscular tube in which digestion is completed
|
|
|
39.
|
Unit of heat used to measure the energy content of food
|
|
|
40.
|
Specific cells in the body to which hormones convey information
|
|
|
41.
|
Responsible for metabolic control, energy balance, and growth
|
|
|
42.
|
Last section of the digestive system from which feces are eliminated
|
|
|
43.
|
Chemical that helps breaks down fats
|
|
|
44.
|
Digestive enzyme found in stomach
|
|
|
45.
|
lowest pH organ
|
|
|
46.
|
A flap that covers the opening to the windpipe during swallowing
|
|
|
47.
|
Series of involuntary muscle contractions along the walls of the digestive
tract
|
|
|
48.
|
Muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach
|
|
|
49.
|
Digestive enzyme found in saliva that breaks down starch
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | hemoglobin | i. | aorta | b. | antigen | j. | platelets | c. | trachea | k. | pulse | d. | nephron | l. | antibody | e. | artery | m. | plasma | f. | atrium | n. | capillary | g. | alveoli | o. | ventricle | h. | urine | p. | vein |
|
|
|
50.
|
Fluid portion of blood in which blood cells move
|
|
|
51.
|
Solution of body wastes consisting of excess water, waste molecules, and excess
ions
|
|
|
52.
|
Regular surge of blood through an artery
|
|
|
53.
|
largest artery
|
|
|
54.
|
A lower chamber of the heart
|
|
|
55.
|
An upper chamber of the heart
|
|
|
56.
|
A large blood vessel that carries blood from the tissues to the heart
|
|
|
57.
|
A kind of large, muscular, thick-walled elastic vessel that carries blood away
from the heart
|
|
|
58.
|
gas exchange takes place in this part of the lungs
|
|
|
59.
|
Microscopic blood vessel
|
|
|
60.
|
Passageway leading from the larynx to the lungs
|
|
|
61.
|
helps with clotting
|
|
|
62.
|
Iron-containing protein that picks up oxygen after it enters the blood vessels
in the lungs
|