Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A dog's phenotype can be determined by _____.
a. | looking at the dog's parents | b. | examining the dog's
chromosomes | c. | mating the dog and examining its offspring | d. | looking at the
dog |
|
|
|
2.
|
What phenotype is depicted in Figure 12-8? 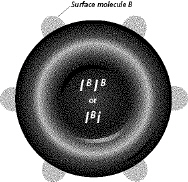 Figure 12-8
|
|
|
3.
|
In Figure 12-7, the trait shown is _____. 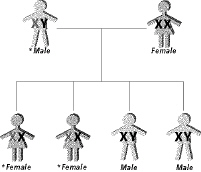 Figure 12-7 a. | not sex-linked | c. | Y-linked | b. | X-linked | d. | trisomy |
|
|
|
4.
|
The _____ produced by each parent are shown along the sides of a Punnett
square.
a. | zygotes | c. | gametes | b. | offspring | d. | hybrids |
|
|
|
5.
|
A white mouse whose parents are both white produces only brown offspring when
mated with a brown mouse. The white mouse is most probably _____.
a. | homozygous recessive | c. | homozygous dominant | b. | heterozygous | d. | haploid |
|
|
|
6.
|
The statement: "In meiosis, the way in which a chromosome pair separates
does not affect the way other pairs separate," is another way of expressing Mendel's law of
_____.
a. | dominance | c. | independent assortment | b. | first filial
generations | d. | Punnett
squares |
|
|
|
7.
|
A trait controlled by four alleles is said to have _____.
a. | homologous alleles | c. | hybridization | b. | autosomes | d. | multiple
alleles |
|
|
|
8.
|
A useful device for predicting the possible offspring of crosses between
different genotypes is the _____.
a. | law of dominance | c. | Punnett square | b. | law of independent
assortment | d. | testcross |
|
|
|
9.
|
The type of inheritance shown when a red-flowering plant is crossed with a
white-flowering plant and only pink-flowering plants are produced is _____.
a. | inbreeding | c. | polygenic inheritance | b. | incomplete
dominance | d. | codominance |
|
|
|
10.
|
The blood types A, B, AB, and O are the result of _____ inheritance.
a. | multiple allelic | c. | sex-linked | b. | polygenic | d. | simple dominant |
|
|
|
11.
|
Cells containing two alleles for each trait are described as _____.
a. | haploid | c. | diploid | b. | gametes | d. | homozygous |
|
|
|
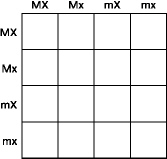 Figure
10-7
|
|
|
12.
|
How should the completed bottom row of Figure 10-7 read?
a. | MMXX, MMXx, MmXX, MmXx | c. | MmXX, mMXx, mmXX, mmXx | b. | MMxX, MMxx, MmxX,
Mmxx | d. | MmXx, Mmxx, mmXx,
mmxx |
|
|
|
13.
|
What fraction of this cross will be dominant for both traits?
|
|
|
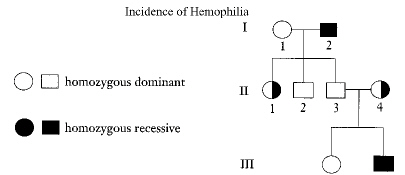 Figure
12-1
|
|
|
14.
|
For the trait being followed in the pedigree, individuals II-1 and II-4 in
Figure 12-1 can be classified as _____.
a. | homozygous dominant | c. | homozygous recessive | b. | mutants | d. | carriers |
|
|
|
15.
|
What type of inheritance pattern does the trait represented by the shaded
symbols in Figure 12-1 illustrate?
a. | incomplete dominance | c. | codominance | b. | multiple alleles | d. | sex-linked |
|
|
|
16.
|
Refer to Figure 12-1. If individual III-2 marries a person with the same
genotype as individual I-1, what is the chance that one of their children will be afflicted with
hemophilia?
|
|
|
17.
|
A phenotype that results from a dominant allele must have at least _____
dominant allele(s) present in the parent(s).
|
|
|
18.
|
A couple has two children, both of whom are boys. What is the chance that the
parents' next child will be a boy?
|
|
|
19.
|
The passing on of traits from parents to offspring is called _____.
a. | genetics | c. | inbreeding | b. | heredity | d. | gene splicing |
|
|
|
20.
|
A child is diagnosed with a rare genetic disease. Neither parent has the
disease. How might the child have inherited the disorder?
a. | The disorder is dominant and was carried by a parent. | b. | The disorder is
recessive and carried by both parents. | c. | The disorder is sex linked and inherited only
from the father. | d. | The disorder could occur only as a mutation in the child because neither parent had
the disease. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The diagram in Figure 10-2 shows a diploid cell with two homologous pairs of
chromosomes. Due to independent assortment, the possible allelic combinations that could be found in
gametes produced by the meiotic division of this cell are _____. (HINT: Dihybrid FOIL) 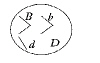 Figure 10-2 Figure 10-2a. | Bb, Dd, BB, and DD | c. | BbDd and
BDbd | b. | BD, bD, Bd, and bd | d. | Bd and bD
only |
|
|
|
22.
|
The law of independent assortment states that the inheritance of alleles for one
trait is not affected by the inheritance of alleles for a different trait if the genes for the traits
are on _____.
a. | separate chromosomes | c. | the same chromosome | b. | homologous chromosomes | d. | homozygous
chromosomes |
|
|
|
23.
|
If a female fruit fly heterozygous for red eyes (XRXr)
crossed with a white-eyed male (XrY), what percent of their offspring would have white
eyes?
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following describes an organism that has the genotype Bb?
a. | homozygous | c. | inbreed | b. | heterozygous | d. | all of these |
|
|
|
25.
|
A man heterozygous for blood type A marries a woman heterozygous for blood type
B. The chance that their first child will have type O blood is _____.
|
|
|
26.
|
Because the gene for red-green color blindness is located on the X chromosome,
it is normally not possible for a _____.
a. | carrier mother to pass the gene on to her daughter | b. | carrier mother to
pass the gene on to her son | c. | color blind father to pass the gene on to his
daughter | d. | color blind father to pass the gene on to his son |
|
|
|
27.
|
In humans, red-green color blindness is _____.
a. | caused by a recessive allele | b. | equally common in both
sexes | c. | inherited in males from their fathers | d. | produced in males by a heterozygous
genotype |
|
|
|
28.
|
When roan cattle are mated, 25% of the offspring are red, 50% are roan, and 25%
are white. Upon examination, it can be seen that the coat of a roan cow consists of both red and
white hairs. This trait is one controlled by _____.
a. | multiple alleles | c. | sex-linked genes | b. | codominant alleles | d. | polygenic
inheritance |
|
|
|
29.
|
A female guinea pig homozygous dominant for black fur color is mated with a male
homozygous for white fur color. In a litter of eight offspring, there would probably be _____.
a. | 8 black guinea pigs | b. | 4 black and 4 white guinea
pigs | c. | 2 black, 4 gray, and 2 white guinea pigs | d. | 8 white guinea
pigs |
|
|
|
30.
|
The gamete that contains genes contributed only by the mother is _____.
a. | the sperm | c. | a zygote | b. | an egg | d. | dominant |
|
|
|
31.
|
In mink, brown fur color is dominant to silver-blue fur color. If a homozygous
brown mink is mated with a silver-blue mink and 8 offspring are produced, how many would be expected
to be silver-blue?
|
|
|
32.
|
Eye color in humans is the result of _____ inheritance.
a. | multiple allelic | c. | sex-linked | b. | polygenic | d. | simple dominant |
|
|
|
33.
|
Mendel's law of segregation states that during meiosis, the factors that
control each trait separate, and only _____ from each pair is/are passed to the offspring.
a. | one factor | c. | two factors | b. | the dominant trait | d. | the recessive
trait |
|
|
|
34.
|
Royal hemophilia is the result of _____ inheritance.
a. | multiple allelic | c. | sex-linked | b. | polygenic | d. | simple dominant |
|
|
|
35.
|
Two healthy parents produce a child with the genetic disorder of cystic
fibrosis, which is the result of a recessive gene. What would be the best explanation for this
inheritance?
a. | This is not the result of a genetic disorder. | b. | Both parents carried
the recessive gene for cystic fibrosis. | c. | Cystic fibrosis is a chromosomal mutation that
occurred during development and is not related to the parental genotypes. | d. | Cystic fibrosis is
caused by a mutation in the 21st pair of chromosomes. |
|
|
|
36.
|
A cross between a white rooster and a black hen results in 100% blue Andalusian
offspring. When two of these blue offspring are mated, the probable phenotypic ratio seen in their
offspring would be _____.
a. | 100% blue | c. | 75% blue, 25% white | b. | 75% black, 25% white | d. | 25% black, 50% blue, 25%
white |
|
|
|
37.
|
The 23rd pair of chromosomes that differ in males and females are called
_____.
a. | autosomes | c. | multiple alleles | b. | sex chromosomes | d. | polygenes |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | crossing over | e. | haploid | b. | meiosis | f. | homozygous | c. | dihybrid | g. | zygote | d. | heredity | h. | fertilization |
|
|
|
38.
|
The passing of characteristics from parents to offspring
|
|
|
39.
|
The alleles present for a trait are the same
|
|
|
40.
|
The type of cell division that produces gametes
|
|
|
41.
|
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
|
|
|
42.
|
The cell produced when a male gamete fuses with a female gamete
|
|
|
43.
|
A cell that contains one member of each chromosome pair
|
|
|
44.
|
A cross involving two different traits
|
|
|
45.
|
The uniting of the male and female gametes
|