Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
In mRNA _____ is used as a nitrogenous base instead of _____, found in
DNA.
a. | Uracil, Thymine | c. | Thymine, Adnine | b. | Guanine, Cytosine | d. | Adnine, Uracil |
|
|
|
2.
|
The codon AUG always signals what event in a cell?
a. | Stopping of protein synthesis | c. | DNA replication | b. | Starting of
protein synthesis | d. | none of
the above |
|
|
|
3.
|
The enzyme ______ unwinds and unzips DNA so replication can occur.
a. | Polymerase | c. | Lactase | b. | Lipase | d. | Helicase |
|
|
|
4.
|
What types of bonds hold amino acids together to make a protein?
a. | hydrogen | c. | super | b. | peptide | d. | covalent |
|
|
|
5.
|
Where does DNA replication take place within the cell?
a. | Endoplasmic Reticulum | c. | Cytoplasum | b. | Nucleus | d. | Not in the cell |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which one of the following nucleotide pair bonds would be found in a DNA
molecule?
a. | adenine-guanine | c. | adenine-cytosine | b. | guanine-cytosine | d. | cytosine-uracil |
|
|
|
7.
|
The backbone of a DNA molecule is made of which two components?
a. | phosphate molecules and ribose sugars | b. | deoxyphosphate molecules and ribose
sugars | c. | phosphate molecules and deoxyribose sugars | d. | deoxyphosphate
molecules and deoxyribose sugars |
|
|
|
8.
|
Ribosomes are made of _____.
a. | rRNA and protein | c. | rRNA and mRNA | b. | tRNA and mRNA | d. | protein and
tRNA |
|
|
|
9.
|
Watson and Crick were the first to suggest that DNA is _____.
a. | a short molecule | c. | a protein molecule | b. | the shape of a double helix | d. | the genetic
material |
|
|
|
10.
|
The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____.
a. | binary fission | c. | replication | b. | mitosis | d. | translation |
|
|
|
11.
|
A DNA nucleotide may be made up of a phosphate group, along with _____.
a. | deoxyribose sugar and uracil | c. | deoxyribose sugar and
thymine | b. | ribose sugar and adenine | d. | ribose sugar and cytosine |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which series is arranged in order from largest to smallest in size?
a. | chromosome, nucleus, cell, DNA, nucleotide | b. | cell, nucleus,
chromosome, DNA, nucleotide | c. | nucleotide, chromosome, cell, DNA,
nucleus | d. | cell, nucleotide, nucleus, DNA, chromosome |
|
|
|
13.
|
X rays, ultraviolet light, and radioactive substances that can change the
chemical nature of DNA are classified as _____.
a. | growth regulators | c. | hydrolytic enzymes | b. | metamorphic molecules | d. | mutagens |
|
|
|
Help Wanted | | Positions Available in the genetics industry.
Hundreds of entry-level openings for tireless workers. No previous experience necessary. Must be able
to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. The ability to work in close association with ribosomes
is a must. | | Accuracy and Speed vital
for this job in the field of translation. Applicants must demonstrate skills in transporting and
positioning amino acids. Salary commensurate with experience. | | Executive Position available. Must be able to maintain
genetic continuity through replication and control cellular activity by regulation of enzyme
production. Limited number of openings. All benefits. | | Supervisor of production of proteins—all shifts. Must be able to follow exact
directions from double-stranded template. Travel from nucleus to the cytoplasm is additional job
benefit. | |
Table 11-1
|
|
|
14.
|
Applicants for the fourth job of the Help Wanted ad in Table 11-1,
"Supervisor," could qualify if they were _____.
|
|
|
15.
|
Applicants for the third job of the Help Wanted ad in Table 11-1,
"Executive Position," could qualify if they were _____.
|
|
|
16.
|
Applicants for the second job of the Help Wanted ad in Table 11-1,
"Accuracy and Speed," could qualify if they were _____.
|
|
|
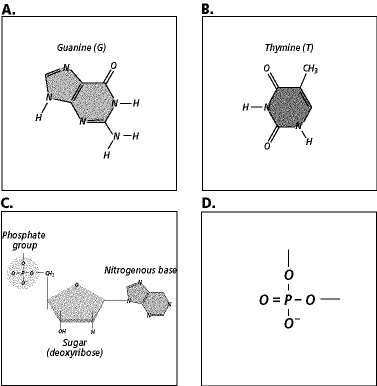 Figure
11-3
|
|
|
17.
|
Which structure shown in Figure 11-3 is a pyrimidine?
|
|
|
18.
|
Which structure shown in Figure 11-3 does not contain a nitrogenous base?
|
|
|
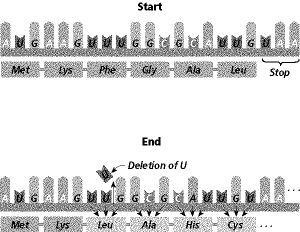 Figure
11-4
|
|
|
19.
|
What type of mutation has occurred in Figure 11-4?
a. | point mutation | c. | lethal | b. | frame shift | d. | protein |
|
|
|
20.
|
What will be the result of the mutation in Figure 11-4?
a. | it will have no affect on protein function | b. | only one amino acid
will change | c. | nearly every amino acid in the protein will be changed | d. | the organism will
die |
|
|
|
21.
|
Figure 12-5 shows the structure of a(an) 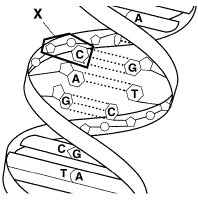
Figure 12–5
a. | DNA molecule. | c. | RNA molecule. | b. | amino acid. | d. | protein. |
|
|
|
22.
|
DNA is copied during a process called
a. | replication. | c. | transcription. | b. | translation. | d. | transformation. |
|
|
|
23.
|
In eukaryotes, DNA
a. | is located in the nucleus. | c. | is located in the
ribosomes. | b. | floats freely in the cytoplasm. | d. | is circular. |
|
|
|
24.
|
RNA contains the sugar
a. | ribose. | c. | glucose. | b. | deoxyribose. | d. | lactose. |
|
|
|
25.
|
Which RNA molecule carries amino acids?
a. | messenger RNA | c. | ribosomal RNA | b. | transfer RNA | d. | RNA polymerase |
|
|
|
26.
|
What is produced during transcription?
a. | RNA molecules | c. | RNA polymerase | b. | DNA molecules | d. | proteins |
|
|
|
27.
|
What does Figure 12-6 show? 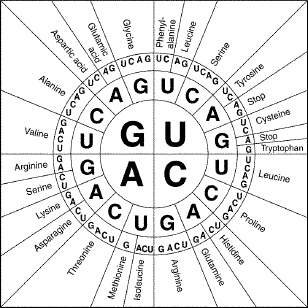 Figure 12-6 Figure 12-6a. | anticodons | b. | the order in which amino acids are
linked | c. | the code for splicing mRNA | d. | the mRNA codons and their associated amino
acids |
|
|
|
28.
|
What happens during the process of translation?
a. | Messenger RNA is made from DNA. | b. | The cell uses information from messenger RNA to
produce proteins. | c. | Transfer RNA is made from messenger
RNA. | d. | Copies of DNA molecules are made. |
|
|
|
29.
|
What does Figure 13-1 show? 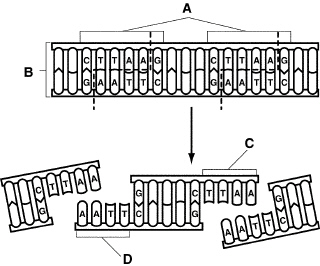
Figure 13–1
a. | gel electrophoresis | b. | DNA sequencing | c. | a restriction enzyme
cutting different sequences of DNA | d. | polymerase chain
reaction |
|
|
|
30.
|
An application of using DNA technology to help environmental scientists would be
_____.
a. | use PCR to analyze DNA at a crime scene | b. | create a tobacco
plant that glows in the dark | c. | clone the gene for human growth hormone to
treat pituitary dwarfism | d. | make transgenic bacteria that can be used to
clean up oil spills more quickly than do the natural bacteria |
|
|
|
31.
|
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to _____.
a. | clone chromosomes of various species | b. | cut DNA into fragments of various
sizes | c. | separate DNA fragments by charge and length | d. | inject foreign DNA
into animal and plant cells |
|
|
|
32.
|
A small amount of DNA obtained from a mummy or from frozen remains of a human
may be cloned. In order to clone small amounts of DNA, _____ needs to be used to generate larger
quantities of the DNA.
a. | polymerase chain reaction techniques | b. | gel electrophoresis | c. | DNA
fingerprinting | d. | gene splicing |
|
|
|
33.
|
Examine the pieces of DNA represented in Figure 13-1. Why are the nucleotide
sequences on both strands referred to as palindromes?  Figure 13-1 a. | the sequences show chromosome mutation | b. | the DNA is an example of a transgenic
codon | c. | the sequences are the same but run in opposite directions | d. | each nucleotide is
represented |
|
|
|
34.
|
What must be on either end of any genetic material that is inserted into the
cleaved DNA in Figure 13-5?  Figure
13-5
|
|
|
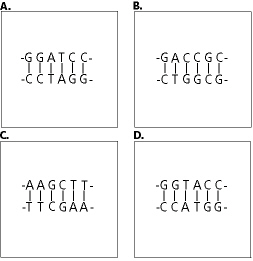 Figure
13-6
|
|
|
35.
|
Which segment in Figure 13-6 is not a palidrome?
|
|
|
36.
|
If the segments in Figure 13-6 are mixed with several restriction enzymes, which
will not be cleaved?
|
|
|
37.
|
According to Figure 13-7, which DNA sequence will be cleaved by EcoRI, which
cuts AATT/TTAA? 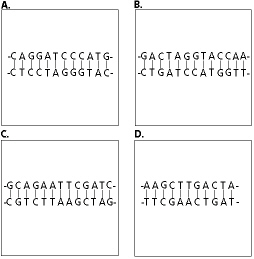 Figure
13-7
|
|
|
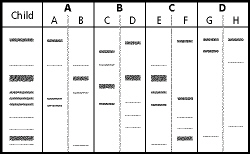 Figure
13-8
|
|
|
38.
|
According to Figure 13-8, which are the parents of the child?
|
|
|
39.
|
According to Figure 13-8, which parents might give a false positive if only the
longer DNA fragments were analyzed?
|