Ch. 13 Prep-Test Gases
Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
What volume will 88 grams of CO2 at a temperature of 300. K and a
pressure of 1.0 atm have?
a. | 49 L | c. | 20 L | b. | 102 L | d. | 75 L |
|
|
|
2.
|
If a gas occupies 950. mL at standard temperature, what volume does it occupy at
546 K if the pressure remains constant?
a. | 475 mL | c. | 1000. mL | b. | 966. mL | d. | 1.90 x 103
mL |
|
|
|
3.
|
Avogadro’s law states that ____.
a. | the volume of a gas varies inversely with the amount (mols.) | b. | the volume of a gas
varies directly with the amount (mols.) | c. | the temperature of a gas varies inversely with
pressure | d. | the temperature of a gas varies directly with
pressure |
|
|
|
4.
|
A sample of gas at 6.0 atm and 298 K increases in temperature to 596 K. If the
volume is unchanged, what is the new pressure?
a. | 5.4 atm | c. | 36 atm | b. | 12 atm | d. | 18 atm |
|
|
|
5.
|
What volume of carbon dioxide gas at 20 ºC and
1.00 atm is produced from 10.0 g of calcium carbonate?
CaCO3(s) --> CaO(s) + CO2(g)
a. | 1.38 L | c. | 22.4 L | b. | 2.40 L | d. | 1.00 L |
|
|
|
6.
|
A sample of nitrogen is collected by water displacement at 730.0 mm Hg and
20ºC. What is the partial pressure of the nitrogen? The water vapor pressure at
20oC is 17.5 torr.
a. | 17.5 mm Hg | c. | 717.2 mm Hg | b. | 712.5 mm Hg | d. | 747.5 mm Hg |
|
|
|
7.
|
Convert the pressure 2.50 atm to kPa.
a. | 1 kPa | c. | 760 kPa | b. | 253 kPa | d. | 1000 kPa |
|
|
|
8.
|
A container with a volume of 750 mL containing 56 g of CO changes to 375 mL.
What happened to the amount of CO if pressure and temperature remained constant? Assume that the
amount of particles in the container CAN change.
a. | remains the same | c. | doubles | b. | is cut in half | d. | not enough data to
answer |
|
|
|
9.
|
A 5.00 mol sample of argon gas occupies 250. mL. What volume does the gas occupy
if the sample is increased to 7.50 mol?
a. | 500. mL | c. | 125 mL | b. | 375 mL | d. | 1000. mL |
|
|
|
10.
|
The pressure of a 1000. mL sample of gas at 27ºC increases from 700. mm Hg
to 1400. mm Hg. If the volume is unchanged, what is the new temperature?
a. | 18ºC | c. | 600ºC | b. | 137ºC | d. | 327ºC |
|
|
|
11.
|
An ideal gas is an imaginary gas
a. | not made of particles. | b. | that conforms to all of the assumptions of the
kinetic theory. | c. | whose particles have zero mass. | d. | made of motionless
particles. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Unlike in an ideal gas, in a real gas
a. | all particles move in the same direction. | b. | all particles have
the same kinetic energy. | c. | the particles cannot
diffuse. | d. | the particles exert attractive forces on each other. |
|
|
|
13.
|
What instrument measures atmospheric pressure?
a. | barometer | c. | vacuum pump | b. | thermometer | d. | torrometer |
|
|
|
14.
|
According to the kinetic-molecular theory, particles of matter
a. | are in constant motion. | c. | have different
colors. | b. | have different shapes. | d. | are always fluid. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Standard pressure is exactly
a. | 1 atm. | c. | 101.325 atm. | b. | 760 atm. | d. | 101 atm. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Under which of the following sets of conditions
will a 0.50 mole sample of helium
occupy a volume of 11.2 liters? a. | 298 K and 0.90 atm. | c. | 373 K and 0.50 atm. | b. | 273 K and 1.10 atm | d. | 273 K and 1.00
atm |
|
|
|
17.
|
Convert the pressure 0.75 atm to mm Hg.
a. | 101.325 mm Hg | c. | 570 mm Hg | b. | 1430 mm Hg | d. | 760 mm Hg |
|
|
|
18.
|
As a balloon is inflated, what happens to the pressure of the gas inside the
balloon?
a. | It increases. | b. | It stays the same. | c. | It
decreases. | d. | The pressure depends on the type of gas in the
balloon. |
|
|
|
19.
|
At 380. mm Hg, a sample of nitrogen gas occupies 600. mL. What volume does the
gas occupy if the temperature remains constant and the pressure increases to 760. mm Hg?
a. | 150. mL | c. | 600. mL | b. | 300. mL | d. | 900. mL |
|
|
|
20.
|
The volume of a sample of oxygen is 300.0 mL when the pressure is 1 atm and the
temperature is 27.0ºC. At what temperature is the volume 600. mL and the pressure 0.500
atm?
a. | 22.0ºC | c. | 0.50 K | b. | 45.0ºC | d. | 27.0ºC |
|
|
|
21.
|
What happens to the volume of a gas when you increase pressure on it?
a. | The volume increases. | b. | The volume decreases. | c. | The volume remains
constant. | d. | It is impossible to tell because all gases are
different. |
|
|
|
22.
|
If the temperature of a fixed quantity and volume of gas changes,
what also changes?
a. | pressure | c. | mass | b. | density | d. | formula |
|
|
|
23.
|
When a container is filled with H 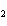 (P H2 = 206
kPa), O 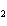 , and N 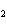
(P N2 = 306 kPa), the pressure in the container is 768 kPa. What is the partial pressure of
O 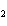 ? a. | 256 kPa | c. | 512 kPa | b. | 128 kPa | d. | 1028 kPa |
|
|
|
24.
|
Why is a gas easier to compress than a liquid or a solid?
a. | Its volume increases more under pressure than an equal volume of liquid
does. | b. | Its volume increases more under pressure than an equal volume of solid
does. | c. | The space between gas particles is much greater than the space between liquid or
solid particles. | d. | The volume of a gas’s particles is the majority of the overall volume of the
gas. |
|
|
|
25.
|
A 30. L sample of gas exerts 200. mm Hg pressure at 273 K. What volume does the
gas have at 100. mm Hg and 546 K?
a. | 90 L | c. | 120 L | b. | 20 L | d. | 240 L |
|
|
|
26.
|
A sample of bromine gas occupies 7.50 L @ STP. How many mols. is this?
a. | .750 mol | c. | .335 mol | b. | 22.4 mol | d. | 1.00 mol |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which law can be used to calculate the number of moles of a contained
gas?
a. | Boyle’s law | c. | ideal gas law | b. | combined gas law | d. | Charles’s
law |
|
|
|
28.
|
The pressure of a sample of helium is 2.0 atm in a 200. mL container. If the
container is compressed to 10. mL without changing the temperature, what is the new pressure?
a. | 200 atm | c. | 100 atm | b. | 0.10 atm | d. | 40. atm |
|
|
|
29.
|
What does the constant bombardment of gas molecules against the inside walls of
a container produce?
a. | temperature | c. | pressure | b. | density | d. | diffusion |
|
|
|
30.
|
If five different gases in a cylinder each exert 1 atm, what is the total
pressure exerted by the gases?
a. | 0.2 atm | c. | 1 atm | b. | 0.5 atm | d. | 5 atm |
|
|
|
31.
|
How is the ideal gas law usually written?
a. | 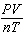 = R = R | c. | PV =
nRT | b. | 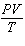 = nR = nR | d. | P = 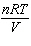 |
|
|
|
32.
|
What happens to the pressure of a gas inside a container if the temperature of
the gas decreases?
a. | The pressure increases. | c. | The pressure
decreases. | b. | The pressure does not change. | d. | The pressure cannot be
predicted. |
|
|
|
33.
|
The volume of a gas is 5.0 L when the temperature is 5.0ºC. If the
temperature is increased to 10.0ºC without changing the pressure, what is the new volume?
a. | 2.5 L | c. | 5.1 L | b. | 4.8 L | d. | 10.0 L |
|