Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | calorimeter | d. | temperature | b. | calorie | e. | specific heat | c. | joule | f. | heat |
|
|
|
1.
|
quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1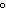 C C
|
|
|
2.
|
SI unit of energy
|
|
|
3.
|
energy transferred between 2 objects because of temperature difference
|
|
|
4.
|
device used to measure the heat absorbed or released during a chemical or
physical process
|
|
|
5.
|
a measure of the random motions of the components of a substance
|
|
|
6.
|
quantity of heat needed to change the temperature of 1 g of a substance by
1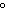 C C
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
7.
|
What happens to the energy produced by burning gasoline in a car engine?
a. | The energy is lost as heat in the exhaust. | b. | The energy is
transformed into work to move the car. | c. | The energy heats the parts of the
engine. | d. | all of the above |
|
|
|
8.
|
How does a calorie compare to a joule?
a. | A calorie is smaller than a joule. | c. | A calorie is equal to a
joule. | b. | A calorie is larger than a joule. | d. | The relationship cannot be
determined. |
|
|
|
9.
|
If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat will be
____.
a. | absorbed by the surroundings | c. | released by the
surroundings | b. | absorbed by the universe | d. | released by the universe |
|
|
|
10.
|
In an exothermic reaction, the energy stored in the chemical bonds of the
reactants is ____.
a. | equal to the energy stored in the bonds of the products | b. | greater than the
energy stored in the bonds of the products | c. | less than the energy stored in the bonds of the
products | d. | less than the heat released |
|
|
|
11.
|
The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of 1 g of a substance by
1 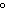 C is defined as ____. a. | a joule | c. | a calorie | b. | specific heat | d. | density |
|
|
|
12.
|
How many calories are in 642 joules? (1 cal = 4.18 J)
a. | 2684 | c. | 154 | b. | 26.84 | d. | 154 000 |
|
|
|
13.
|
How many joules are in 148 calories? (1 cal = 4.18 J)
a. | 6.61 J | c. | 148 J | b. | 35.4 J | d. | 619 J |
|
|
|
14.
|
The specific heat of silver is 0.24 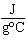 . How many joules of energy
are needed to warm 4.37 g of silver from 25.0 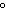 C to 27.5 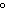 C? a. | 2.62 J | c. | 45.5 J | b. | 0.14 J | d. | 0.022 J |
|
|
|
15.
|
On what principle does calorimetry depend?
a. | the principle of hotness | c. | law of dynamics | b. | law of conservation
of energy | d. | law of multiple
proportions |
|
|
|
16.
|
Two metals of equal mass with different heat capacities are subjected to the
same amount of heat. Which undergoes the smallest change in temperature?
a. | The metal with the higher heat capacity. | b. | The metal with the
lower heat capacity. | c. | Both undergo the same change in
temperature. | d. | You need to know the initial temperatures of the metals. | e. | You need to know
which metals you have. |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the specific heat capacity of gold if it requires 48.8 J to raise the
temperature of 15 grams of gold 25oC?
a. | 29 J/goC | c. | 79 J/goC | b. | 0.13 J/goC | d. | 0.011
J/goC |
|
|
|
18.
|
When solid KBr is dissoved in water, the solution gets colder. This is an
example of a(n) ________ reaction.
a. | endothermic | c. | thermal nuclear | b. | exothermic | d. | exdothermic |
|
|
|
19.
|
Natural gas (CH4) is burned in a furnace
a. | endothermic | c. | thermal nuclear | b. | exothermic | d. | exdothermic |
|
|
|
20.
|
The energy transferred between samples of matter because of a difference in
their temperatures is called
a. | heat. | c. | chemical kinetics. | b. | thermochemistry. | d. | temperature. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which expression defines specific heat?
a. | heat ´ mass ´
temperature change | c. | 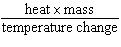
| b. |  | d. | 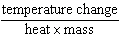 |
|
|
|
22.
|
The Greek letter D stands for
a. | "heat stored in." | c. | "rate
of." | b. | "mass of." | d. | "change in." |
|
|
|
23.
|
The study of all energy changes is called
a. | thermodynamics. | c. | entropy. | b. | enthalpy. | d. | temperature. |
|
|
|
24.
|
Temperature is
a. | associated with the sensation of hot and cold. | b. | proportional to the
average kinetic energy of molecules. | c. | measured with thermometers. | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
25.
|
According to the first law of thermodynamics,
a. | there is no such thing as a perpetual motion machine. | b. | the energy of a
system is constant. | c. | the total energy used in any process is
conserved. | d. | in any process there is a decrease in potential
energy. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a. | Energy as heat flows from a lower temperature to a higher
temperature. | b. | Energy as heat flows from a higher temperature to a lower
temperature. | c. | The amount of heat in a closed system is a constant. | d. | Energy as heat
flowing into an object is determined by the amount of work done on the
object. |
|
|
|
27.
|
In a calorimeter, the energy content of a substance is calculated from
measurement of the temperature change in a known mass of
a. | iron. | c. | water. | b. | air. | d. | steel. |
|
|
|
28.
|
What units are used to measure heat?
a. | joules/mole or kilojoules/mole | c. | joules or
kilojoules | b. | kelvins or degrees Celsius | d. | None of the above |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.
|
Which experiment above illustrates how different amounts of energy result in
different temperature changes when the mass of water is constant?
a. | Experiment 1 | c. | Experiment 3 | b. | Experiment 2 | d. | None of them |
|
True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
30.
|
The quantity of energy is increased as energy is used.
|
|
|
31.
|
Endothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings.
|
|
|
32.
|
In a calorimetry experiment, the system is thermally isolated from the
surroundings.
|
|
|
33.
|
If a person tries to lift a heavy box for 5 seconds and can't make it
budge, the work done on the box is equal to the amount of energy the person uses.
|
|
|
34.
|
In all cooling systems, energy as heat is transferred from one substance to
another, leaving the first substance with less energy and with a lower temperature.
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.
|
It takes more energy as heat to raise the temperature of water by one degree
than to raise the temperature of steam by the same amount.
|
|
|
36.
|
When a substance evaporates it adds energy as heat to its surroundings.
|