|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
In the figure of a voltaic cell shown above, on which side is oxidation taking
place?
|
|
|
2.
|
What would be the expected oxidation state of a group I metal when it is in an
ionic compound?
|
|
|
3.
|
A species whose oxidation number increases in a reaction is
a. | oxidized. | b. | reduced. | c. | autooxidized. | d. | electrolyzed. |
|
|
|
4.
|
In the reaction, 2Cs + Br2 ® 2CsBr,
the oxidizing agent is
|
|
|
Relative Strength of
Oxidizing and Reducing Agents | | Reducing Agents | Oxidizing Agents | | S Li | Li+
W | | T K | K+
E | | R Ca | Ca2+
A | | O Na | Na+
K | | N Mg | Mg2+
E | | G Al | Al3+
R | | E Zn | Zn2+ | | R Cr | Cr3+ | | Fe | Fe2+ | | Ni | Ni2+ | | Sn | Sn2+ | | Pb | Pb2+ | | H2 | H3O+ | |
H2S | S | | Cu | Cu2+ | | I– | I2 | |
MnO42– | MnO4– | | Fe2+ | Fe3+ | | Hg | Hg22+ | | Ag | Ag+ | | NO2– | NO3–
S | | Br– | Br2
T | | W Mn2+ | MnO2
R | | E SO2 | H2SO4
(conc.) O | | A Cr3+ | Cr2O72–
N | | K Cl– | Cl2
G | | E Mn2+ | MnO4–
E | | R F– | F2
R | | |
|
|
|
5.
|
In the figure above, which ion oxidizes Sn to Sn2+ but does NOT
oxidize Hg to Hg22+?
a. | NO3– | b. | Cr2O72– | c. | Al3+ | d. | Fe3+ |
|
|
|
6.
|
In the figure above, which ion is reduced by Zn but not reduced by Ag?
|
|
|
7.
|
What is the oxidation state of iron in iron (II) chloride?
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.
|
Calculate E0 for the reaction of battery
with a silver electrode and a zinc electrode.
a. | –.76V | b. | +.76 V | c. | +.04 V | d. | +1.56
V |
|
|
|
9.
|
Calculate E0 for the reaction,
Hg2+(aq) + Sn(s) ® Sn2+(aq) + Hg(l),
a. | +.66 V | b. | -.14 V | c. | +..8 V | d. | +.99
V |
|
|
|
10.
|
In the reaction F2 + Mg ®
2F– + Mg2+, which species is reduced?
a. | Mg only | b. | F2 only | c. | both Mg and
F2 | d. | neither Mg nor F2 |
|
|
|
11.
|
What are the oxidation numbers in the ion
Cr2O72– ?
a. | Cr = +4, O = –2 | b. | Cr = +6, O = –2 | c. | Cr = +7, O =
–2 | d. | Cr = +2, O = –7 |
|
|
|
12.
|
During redox reactions, reducing agents
a. | keep the same oxidation number. | c. | increase their oxidation
number. | b. | do not participate. | d. | decrease their oxidation number. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Consider the following
reaction: Ba(s) + F2(g) ® BaF2,
The fluorine atoms a. | loses electrons | b. | loses protons | c. | gain electrons | d. | gains
protons |
|
|
|
14.
|
Electrons will be drawn away from the molecule, atom or ion with
a. | the most electrons | c. | the greater electronegativity | b. | the lower
electronegativity | d. | no
electronegativity |
|
|
|
15.
|
Where does oxidation take place in an electrochemical cell?
a. | the cathode | c. | the half-cell | b. | the anode or the cathode | d. | the anode |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following
reactions does not involve oxidation-reduction? a. | Zn + 2HCl ® ZnCl2 +
H2 | c. | CH4 + 3O2 ® 2H2O +
CO4 | b. | 2Na + 2H2O ® 2NaOH +
H2 | d. | FeCl2 + 2NaOH ® Fe(OH)2 + 2
NaCl |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
a. | 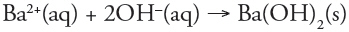 | b. | 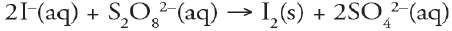 | c. | 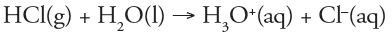 | d. | 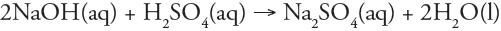 | e. | all are redox reactions |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following statements is true?
Oxidation and reduction a. | do not accompany any chemical changes | c. | accompany all chemical
changes | b. | occur independently of each other | d. | must occur
together |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which is the strongest reducing agent among the elements?
a. | fluorine | b. | cesium | c. | magnesium | d. | iodine |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following is
true for a galvanic cell based on the following reaction?
Zn(s) +
Cu2+(aq)
® Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) a. | The copper serves as the cathode. | c. | The zinc serves as the
cathode. | b. | The zinc is being reduced. | d. | The copper is being oxidized. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The flow of electrons from a battery is the result of
a. | galvani reactions. | c. | electromagnetic reactions. | b. | redox
reactions. | d. | acid-base
reactions. |
|
|
|
22.
|
The reaction Fe ® Fe3+ +
3e–, is a(n) _______________ half reaction
a. | basic | b. | reduction | c. | acidic | d. | oxidation |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which is the most electronegative among the elements?
a. | lithium | b. | iodine | c. | fluorine | d. | cesium |
|
|
|
24.
|
The reduction half reaction for 8NH3 + 6NO2 ® 7N2 + 12H2O is
a. | 8N3- ® 4N2 +
24e- | c. | 8N3- ® 4N2 +
3e- | b. | 6N4+ + 24e- ®
3N2 | d. | 6N4+ + 4e- ®
3N2 |
|
|
|
25.
|
What are the oxidation numbers in the compound KOH?
a. | +1, -2, +1 | b. | 0, 0, 0 | c. | +2, -1, +2 | d. | +1, -1,
+1 |
|
|
|
26.
|
What are the oxidation numbers in the compound SO2?
a. | S = +4, O = –2 | b. | S = +2, O = –2 | c. | S = –2, O = +1 | d. | S = +2, O =
–1 |
|
|
|
27.
|
In the reaction, 3Mg + N2 ®
Mg3N2 , the reducing agent is
a. | Mg | b. | N2 | c. | Mg3N2 | d. | none are
correct |
|
|
|
28.
|
In which case below does nitrogen have an oxidation state of -1?
a. | NH2OH | b. | N2O4 | c. | HNO2 | d. | HNO3 |
|