Multiple Choice
Identify the letter of the choice that best
completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the illustrations above represents a fission reaction?
|
|
|
2.
|
Which of the following is a fusion reaction?
a. | uranium-235 absorbing a neutron and splitting into xenon-140, strontium-94, and two
neutrons | b. | hydrochloric acid combining with sodium hydroxide to form NaCl and
water | c. | carbon-14 decaying into nitrogen-14 and a beta particle | d. | curium-246 combining
with carbon-12 to form nobelium-254 and four neutrons |
|
|
|
3.
|
The energy released in a nuclear reaction comes from
a. | electrons. | c. | positrons. | b. | bonds. | d. | the binding energy of the
nucleus. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Particles or electromagnetic radiation emitted from the nucleus during
radioactive decay
a. | is harmless nuclear fallout. | c. | is
transmutation. | b. | is nuclear radiation. | d. | are daughter nuclides. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which of the following processes always decreases the number of protons by an
even number?
a. | fusion | c. | alpha decay | b. | beta decay | d. | fission |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following lists ranks nuclear radiation from most massive to least
massive?
a. | alpha, beta, and gamma | c. | gamma, alpha, and beta | b. | beta, gamma, and
alpha | d. | gamma, beta, and
alpha |
|
|
|
7.
|
What is the half-life of an isotope if 125 g of a 500 g sample of the isotope
remains after 3.0 years?
a. | 1.5 years | c. | 3.5 years | b. | 2.5 years | d. | 4.5 years |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which series consists of radioactive nuclides produced by successive radioactive
decay until a stable nuclide is reached?
a. | parent series | c. | nuclide series | b. | half-life series | d. | decay series |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following has the weakest penetration abilty?
a. | alpha particles | c. | gamma rays | b. | beta particles | d. | All have the same penetrating
ability. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following has the greatest penetrating ability?
a. | alpha particles | c. | gamma rays | b. | beta particles | d. | All have the same penetrating
ability. |
|
|
|
11.
|
Which of the following is the purpose of a Geiger counter?
a. | illustrate a decay series | c. | record stokres on the golf
course | b. | record half lives | d. | detect radiation |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following is a fission reaction?
a. | hydrogen-2 and hydrogen-3 combining to form a helium-4 atom and a
neutron | b. | carbon-12 and hydrogen-1 combining to form a nitrogen-13 atom | c. | uranium-235
absorbing a neutron and breaking into barium-141, krypton-92, and three neutrons | d. | a glucose molecule
being metabolized with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water |
|
|
|
13.
|
An unstable nucleus ____.
a. | increases its nuclear mass by fission | c. | emits energy when it
decays | b. | increases its half-life | d. | expels all of its protons |
|
|
|
14.
|
What particle is emitted in alpha radiation?
a. | electron | c. | helium nucleus | b. | photon | d. | hydrogen
nucleus |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the change in the atomic number when an atom emits an alpha
particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | increases by 1 | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 2 |
|
|
|
16.
|
What is the change in atomic number when an atom emits a beta particle?
a. | decreases by 2 | c. | increases by 2 | b. | decreases by 1 | d. | increases by 1 |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which symbol is used for an alpha particle?
|
|
|
18.
|
What symbol is used for beta radiation?
|
|
|
19.
|
What particle is needed to complete this nuclear reaction? 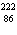 Rn 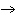 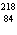 Po + _____
|
|
|
20.
|
When radium-226 (atomic number 88) decays by emitting an alpha particle, it
becomes ____.
a. | polonium-222 | c. | radium-222 | b. | polonium-224 | d. | radon-222 |
|
|
|
21.
|
What particle does argon-39 (atomic number 18) emit when it decays to
potassium-39 (atomic number 19)?
a. | neutron | c. | gamma rays | b. | beta particle | d. | alpha particle |
|
|
|
22.
|
What particle is needed to complete the following nuclear equation?  Mn 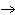 ____ + 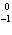 e
|
|
|
23.
|
What particle is needed to complete the following equation? 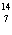 N
+ ____  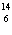 C + 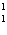 H
|
|
|
24.
|
To what element does polonium-208 (atomic number 84) decay when it emits an
alpha particle?
|
|
|
25.
|
Which of the following is the parent nuclide? 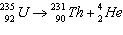
|
|
|
26.
|
Which of the following is the daughter nucleus? 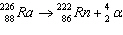
|
|
|
27.
|
The half-life of radon-222 is about four days. What percent of a sample would
you expect to find after 12 days?
|
|
|
28.
|
If the half-life of sodium-24 is 15 hours, how much remains from a 10.0-g sample
after 60 hours?
a. | 0.625g | c. | 0.313g | b. | 2.50g | d. | 1.25g |
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.
|
Consider the diagram above. Which letter best represents the penetrating ability
of beta particles?
a. | A | c. | C | b. | B | d. | none are
correct |
|
|
|
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a
method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of
radiocarbon (14C), a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was developed by
Willard Libby in the late 1940s and soon became a standard tool for archaeologists. Libby received
the Nobel Prize for his work in 1960. The radiocarbon dating method is based on the fact that
radiocarbon is constantly being created in the atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with
atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting radiocarbon combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive
carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire
14C by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with
its environment, and from that point onwards the amount of 14C it contains begins to
decrease as the 14C undergoes radioactive decay.
Measuring the amount of
14C in a sample from a dead plant or animal such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone
provides information that can be used to calculate when the animal or plant died. The older a sample
is, the less 14C there is to be detected, and because the half-life of 14C (the
period of time after which half of a given sample will have decayed) is about 5,730 years, the oldest
dates that can be reliably measured by radiocarbon dating are around 50,000 years ago, although
special preparation methods occasionally permit dating of older samples.
|
|
|
30.
|
Use the above reading to help answer this question.
Nitrogen-14 is
the daughter that is produced during the decay of Carbon-14, what type of particle is also
emitted?
a. | Alpha | c. | Gamma | b. | Beta | d. | Neutron |
|
|
|
31.
|
Use the above reading to help answer this question.
A mastedon
tusk was found near Great Oak High School. The carbon-14 content was found to be 1/4 of the
suspected original amount. Approximately how old is the tusk?
a. | 12,000 yrs old | c. | 6,000 yrs old | b. | 24,000 yrs old | d. | Younger than Mr.
Noble |
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.
|
An archaelogist finds a sample she suspects is 30,000 years old. Using the
above table, what type of radioactive isotope should she use to accurately determine the age of the
sample?
a. | U-235 | c. | Th-232 | b. | C-14 | d. | K-40 |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | positron | c. | beta particle | b. | alpha particle | d. | gamma radiation |
|
|
|
33.
|
particle of charge +1 and mass equal to that of an electron
|
|
|
34.
|
emitted helium nucleus
|
|
|
35.
|
negatively charged radioactive particle.
|
|
|
36.
|
high-energy photons emitted by a radioisotope
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | fission | c. | Geiger counter | b. | fusion | d. | radioisotope |
|
|
|
37.
|
element with unstable nucleus
|
|
|
38.
|
combination of two nuclei to form a nucleus of greater mass
|
|
|
39.
|
radiation detector that makes use of a gas-filled metal tube
|
|
|
40.
|
splitting of nucleus into smaller fragments
|