Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Acids taste
a. | sweet. | c. | bitter. | b. | sour. | d. | salty. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Acids make blue litmus paper turn
a. | red. | c. | blue. | b. | yellow. | d. | black. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Acids react with
a. | bases to produce salts and water. | c. | water to produce bases and
salts. | b. | salts to produce bases and water. | d. | neither bases, salts, nor
water. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Bases feel
a. | rough. | c. | slippery. | b. | moist. | d. | dry. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The traditional (1st) definition of acids is based on the observations of
a. | Brønsted and Lowry. | c. | Arrhenius. | b. | Lewis. | d. | Faraday. |
|
|
|
6.
|
A substance that ionizes nearly completely in aqueous solutions and produces
H+ is a
a. | weak base. | c. | weak acid. | b. | strong base. | d. | strong acid. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is NOT a strong acid?
a. | HNO3 | c. | H2SO4 | b. | CH3COOH | d. | HCl |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following is a diprotic acid?
a. | H2SO4 | c. | HCl | b. | CH3COOH | d. | H3PO4 |
|
|
|
9.
|
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is
a. | an electron-pair acceptor. | c. | a proton
acceptor. | b. | an electron-pair donor. | d. | a proton donor. |
|
|
|
10.
|
In the equation HCl(g) + H2O(l) ® H3O+(aq) + Cl–(aq),
which species is a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
a. | HCl | c. | Cl– | b. | Na2O | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
11.
|
A conjugate base is the species that
a. | remains after a base has given up a proton. | b. | is formed by the
addition of a proton to a base. | c. | is formed by the addition of a proton to an
acid. | d. | remains after an acid has given up a proton. |
|
|
|
12.
|
A species that is formed when a base gains a proton is a
a. | conjugate base. | c. | strong base. | b. | conjugate acid. | d. | strong acid. |
|
|
|
13.
|
In the reaction HF + H 2O 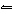 H 3O + +
F –, a conjugate acid-base pair is a. | HF and H2O. | c. | H3O+ and H2O. | b. | F– and
H3O+. | d. | HF and H3O+. |
|
|
|
14.
|
In the reaction HClO 3 + NH 3 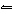
NH 4+ + ClO 3–, the conjugate acid of NH 3
is a. | HClO3. | c. | NH4+. | b. | ClO3–. | d. | not shown. |
|
|
|
15.
|
In the reaction HClO 3 + NH 3 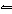
NH 4+ + ClO 3–, the conjugate base of
HClO 3 is a. | ClO3–. | c. | NH4+. | b. | NH3. | d. | not shown. |
|
|
|
16.
|
A species that can react as either an acid or a base is a(n)
a. | Lewis acid. | c. | oxyacid. | b. | amphoteric substance. | d. | organic
substance. |
|
|
|
17.
|
In the reaction HSO 4– + H 2O 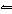 H 3O + + SO 42–, the ion
HSO 4– acts as a(n) a. | acid. | c. | spectator species. | b. | base. | d. | salt. |
|
|
|
18.
|
In the reaction H 3PO 4 + H 2O 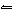
H 3O + + H 2PO 4–, the molecule
H 2O acts as a(n) a. | acid. | c. | spectator species. | b. | base. | d. | salt. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The substances produced when KOH(aq) neutralizes HCl(aq)
are
a. | HClO(aq) and KH(aq). | c. | H2O(l) and
KCl(aq). | b. | KH2O+(aq) and
Cl–(aq). | d. | H3O+(aq) and
KCl(aq). |
|
|
|
20.
|
Pure water can partially break down into charged particles in a process
called
a. | hydration. | c. | self-ionization. | b. | hydrolysis. | d. | dissociation. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which expression represents the pH of a solution?
a. | log[H+] | c. | log[OH–] | b. | –
log[H+] | d. | – log[OH–] |
|
|
|
22.
|
If [H+] of a solution is greater than
[OH–], the solution
a. | is always acidic. | c. | is always neutral. | b. | is always basic. | d. | might be acidic, basic, or
neutral. |
|
|
|
23.
|
The pH scale in general use ranges from
a. | 0 to 1. | c. | 0 to 7. | b. | –1 to 1. | d. | 0 to 14. |
|
|
|
24.
|
The pH of a basic solution is
a. | less than 0. | c. | greater than 7. | b. | less than 7. | d. | greater than
14. |
|
|
|
25.
|
What is the pH of a 1 x 10–5 M KOH solution?
|
|
|
26.
|
If [H+] = 1.00 x 10–5 M, what is the pH of
the solution?
|
|
|
27.
|
What is the pH of a 0.001 M KOH solution?
|
|
|
28.
|
What is the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution whose pH is 4.00?
a. | 1.0 x 10–10 M | c. | 6.0 x 10–4
M | b. | 5.0 x 10–6 M | d. | 1.0 x 10–4
M |
|
|
|
29.
|
A reaction in which products can react to re-form reactants is
a. | at equilibrium. | c. | buffered. | b. | reversible. | d. | impossible. |
|
|
|
30.
|
At equilibrium,
a. | all reactions have ceased. | b. | only the forward reaction
continues. | c. | only the reverse reaction continues. | d. | both the forward and reverse reactions
continue. |
|
|
|
31.
|
At equilibrium, the total amount of the product(s)
a. | is always equal to the total amount of the reactants. | b. | is always greater
than the total amount of the reactants. | c. | is always less than the total amount of the
reactants. | d. | may be equal to, greater than, or less than the total amount of the
reactants. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which symbol represents the equilibrium constant?
|
|
|
33.
|
A very low value of K indicates that
a. | equilibrium is reached slowly. | c. | reactants are
favored. | b. | products are favored. | d. | equilibrium has been reached. |
|
|
|
34.
|
In the equation 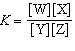 , what represents the concentrations of the
reactants? a. | [Y] and [Z] | c. | 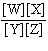 | b. | [W] and
[X] | d. | 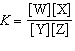 |
|
|
|
35.
|
How do coefficients from a chemical equilibrium appear when the chemical
equilibrium expression is written?
a. | as coefficients | c. | as subscripts | b. | as exponents | d. | They do not
appear. |
|
|
|
36.
|
What is the chemical equilibrium expression for the equation
2A 2B + 3CD 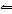 A 4D + C 3B 2?
|
|
|
37.
|
An equilibrium mixture of SO 2, O 2, and SO 3
gases is determined to consist of 2 mol/L SO 2, 1 mol/L
O 2, and 4 mol/L SO 3. What is the equilibrium constant for the system at this
temperature? The balanced equation for this reaction is 2SO 2( g) +
O 2( g) 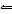 2SO 3( g).
|
|
|
38.
|
If the pressure on the equilibrium system 2CO( g) +
O 2( g) 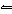 2CO 2( g) is increased, a. | the quantity of CO(g) increases. | b. | the quantity of
CO2(g) decreases. | c. | the quantity of CO2(g)
increases. | d. | the quantities in the system do not change. |
|
|
|
39.
|
If the temperature of the equilibrium system CH 3OH( g) + 101 kJ
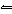 CO( g) + 2H 2( g) increases, a. | [CH3OH] increases and [CO]
decreases. | b. | [CH3OH] decreases and [CO]
increases. | c. | [CH3OH] increases and [CO]
increases. | d. | the concentrations in the system do not change. |
|
|
|
40.
|
If the temperature of the equilibrium system CH 3OH( g) + 101 kJ
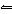 CO( g) + 2H 2( g) increases, Ka. | increases. | c. | increases or decreases. | b. | decreases. | d. | does not change. |
|
|
|
41.
|
If a reaction system has come to equilibrium, it can be made to run to
completion
a. | only if it is not reversible. | c. | by applying Le
Châtelier's principle. | b. | only if the temperature is low
enough. | d. | under no
circumstances. |
|
|
|
42.
|
What is the equilibrium constant, K, for the ionization of acetic acid,
shown in the reaction CH 3COOH( aq) + H 2O (l) 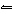 H 3O +( aq) +
CH 3COO –( aq)? a. | [H3O+]
[CH3COOH–] | c. | 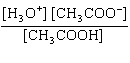
| b. | 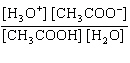 | d. | 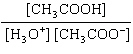 |
|
|
|
43.
|
The pH of a solution is 12. What is its [OH-]?
a. | 1 x 10–12 M | c. | 0.01 M | b. | 1 x
10–7 M | d. | 12
M |
|
Matching
|
|
|
|
|
|
44.
|
Represents the activation energy of the forward reaction.
|
|
|
45.
|
Represents the potential energy of the activated complex.
|
|
|
46.
|
Represents the potential energy of the reactants.
|
|
|
47.
|
Represents the change in energy of the forward and reverse reaction.
|
|
|
48.
|
Represents the activation energy of the reverse reaction.
|