Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The number of atoms in a mole of any pure substance is called
a. | its atomic number. | c. | its mass number. | b. | Avogadro’s number. | d. | its gram-atomic
number. |
|
|
|
2.
|
What can be said about 1 mol Ag and 1 mol Au?
a. | They are equal in mass. | b. | They contain the same number of
atoms. | c. | Their molar masses are equal. | d. | They have the same atomic
mass. |
|
|
|
3.
|
An Avogadro’s number of any element is equivalent to
a. | the atomic number of that element. | c. | 6.022 ´ 1023 particles. | b. | the mass number of that
element. | d. | 12 g of that
element. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Using a periodic table, what is the average atomic mass of zinc?
a. | 69.723 amu | c. | 63.546 amu | b. | 58.693 amu | d. | 65.39 amu |
|
|
|
5.
|
The atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.008 amu. The reason that this value is not a
whole number is that
a. | hydrogen only exists as a diatomic molecule. | b. | the mass of hydrogen
is the sum of the masses of the protons and electrons in the atom. | c. | the mass of a proton
is not exactly equal to 1 amu. | d. | hydrogen has more than one
isotope. |
|
|
|
6.
|
A chemical formula includes the symbols of the elements in the compound and
subscripts that indicate
a. | the number of formula units present. | b. | the number of atoms or ions of each
type. | c. | the formula mass. | d. | the charges on the elements or
ions. |
|
|
|
7.
|
A formula that shows the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms in a compound
is the
a. | molecular formula. | c. | structural formula. | b. | ideal formula. | d. | empirical
formula. |
|
|
|
8.
|
To determine the molar mass of an element, one must know the
element’s
a. | Avogadro number. | c. | number of isotopes. | b. | atomic number. | d. | average atomic
mass. |
|
|
|
9.
|
What is the molar mass of magnesium?
a. | 12.00 g | c. | 24.305 g | b. | 26.982 g | d. | 22.990 g |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the empirical formula for a compound that is 31.9% potassium,
28.9% chlorine, and 39.2% oxygen?
a. | KClO2 | c. | K2Cl2O3 | b. | KClO3 | d. | K2Cl2O5 |
|
|
|
11.
|
A compound contains 64 g of O and 4 g of H. What is the empirical formula for
this compound?
|
|
|
12.
|
A molecular compound has the empirical formula XY3. Which of the
following is a possible molecular formula?
|
|
|
13.
|
A compound’s empirical formula is NO2. If the formula mass is
92 amu, what is the molecular formula?
|
|
|
14.
|
What is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula for a
compound?
a. | molecular mass | c. | atomic mass | b. | formula mass | d. | actual mass |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the formula mass of ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH?
a. | 30.33 amu | c. | 45.06 amu | b. | 33.27 amu | d. | 46.08 amu |
|
|
|
16.
|
The molar mass of LiF is 25.94 g/mol. How many moles of LiF are present in 10.37
g?
a. | 0.3998 mol | c. | 2.500 mol | b. | 1.333 mol | d. | 36.32 mol |
|
|
|
17.
|
How many oxygen atoms are there in 0.500 mol of CO2?
a. | 6.02 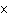 1023
1023 | c. | 15.9994 | b. | 3.01 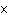 1023
1023 | d. | 11.0 |
|
|
|
18.
|
If 0.500 mol of Na+ combines with 0.500 mol of Cl–
to form NaCl, how many formula units of NaCl are present?
a. | 3.01 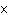 1023 1023 | c. | 6.02 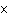 1024
1024 | b. | 6.02 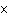 1023 1023 | d. | 1 |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the percentage composition of CuCl2?
a. | 33% Cu, 66% Cl | c. | 65.50% Cu, 34.50% Cl | b. | 50% Cu, 50% Cl | d. | 47.27% Cu, 52.73%
Cl |
|
|
|
20.
|
The empirical formula is always the accepted formula for a(n)
a. | atom. | c. | molecular compound. | b. | molecule. | d. | ionic compound. |
|
|
|
21.
|
A positively charged particle with mass 1.673 ´
10–24 g is a(n)
a. | proton. | c. | electron. | b. | neutron. | d. | positron. |
|
|
|
22.
|
All atoms of the same element have the same
a. | atomic mass. | c. | mass number. | b. | number of neutrons. | d. | atomic number. |
|
|
|
23.
|
Atoms of the same element can differ in
a. | chemical properties. | c. | atomic number. | b. | mass number. | d. | number of protons and
electrons. |
|
|
|
24.
|
In determining atomic mass units, the standard is the
a. | C-12 atom. | c. | H-1 atom. | b. | C-14 atom. | d. | O-16 atom. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The abbreviation for atomic mass unit is
|
|
|
26.
|
The average atomic mass of an element is the average of the atomic masses of
its
a. | naturally occurring isotopes. | c. | nonradioactive
isotopes. | b. | two most abundant isotopes. | d. | artificial isotopes. |
|
|
|
27.
|
A single atom of an isotope does not have a(n)
a. | relative atomic mass. | c. | mass number. | b. | atomic number. | d. | average atomic
mass. |
|
|
|
28.
|
The mass of two moles of oxygen atoms (atomic mass 16 amu) is
a. | 16 g. | c. | 48 g. | b. | 32 g. | d. | 64 g. |
|
|
|
29.
|
How many moles of atoms are in 50.15 g of mercury (atomic mass 200.59
amu)?
a. | 0.1001 mol | c. | 0.2500 mol | b. | 0.1504 mol | d. | 0.4000 mol |
|
|
|
30.
|
The molar mass of MgI2 is
a. | the sum of the masses of 1 mol of Mg and 2 mol of I. | b. | the sum of the
masses of 1 mol of Mg and 1 mol of I. | c. | the sum of the masses of 1 atom of Mg and 2
atoms of I. | d. | the sum of the masses of 1 atom of Mg and 1 atom of
I. |
|
|
|
31.
|
A formula that shows the simplest whole-number ratio of the atoms in a compound
is the
a. | molecular formula. | c. | experimental formula. | b. | ideal
formula. | d. | empirical
formula. |
|
|
|
32.
|
What is the empirical formula for a compound that is 53.3% O and 46.7%
Si?
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the molecular formula of a compound that has a formula mass of 50.48 amu
and an empirical formula of CH3Cl?
a. | CHCl | c. | CH3Cl | b. | CH2Cl | d. | CH2Cl2 |
|
|
|
34.
|
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different
a. | principal chemical properties. | c. | numbers of
protons. | b. | masses. | d. | numbers of electrons. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The molar mass of CS2 is 76.15 g/mol. How many grams of
CS2 are present in 10.00 mol?
a. | 0.13 g | c. | 10.00 g | b. | 7.614 g | d. | 761.5 g |
|
|
|
36.
|
The molar mass of NH3 is 17.03 g/mol. How many moles of
NH3 are present in 107.1 g?
a. | 0.1623 mol | c. | 6.289 mol | b. | 3.614 mol | d. | 107.1 mol |
|
|
|
37.
|
What is the mass of 0.240 mol glucose,
C6H12O6?
a. | 24.0 g | c. | 180.16 g | b. | 43.2 g | d. | 750. g |
|
|
|
38.
|
How many Cl– ions are present in 2.00 mol of KCl?
a. | 1.20 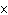 1024 1024 | c. | 2.00 | b. | 6.02 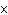 1024
1024 | d. | 0.5 |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which of the following compounds have the same empirical formula?
a. | NO2 and N2O5 | c. | C5H10 and
C3H6 | b. | SO3 and
NO3 | d. | H2O and H2O2 |
|