Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
General Solubility
Guidelines | 1. Most sodium, potassium, and ammonium compounds are soluble in
water. | 2. Most nitrates, acetates, and chlorates are soluble. | 3. Most chlorides are
soluble, except those of silver, mercury(I), and lead. Lead(II) chloride is soluble in hot
water. | 4. Most sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, and
lead. | 5. Most carbonates, phosphates, and silicates are insoluble, except those of
sodium, potassium, and ammonium. | 6. Most sulfides are insoluble, except those of calcium,
strontium, sodium, potassium, and ammonium. | |
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following pairs of solutions produces a precipitate when
combined?
a. | KOH and NH4Cl | c. | Na2SO4 and
KCl | b. | Fe(NO)3 and KCl | d. | NH4Cl and AgNO3 |
|
|
|
2.
|
When solutions of NH4OH and K2SO4 are combined,
what precipitate(s) forms?
a. | (NH4)2SO4 | c. | (NH4)2SO4 and KOH | b. | KOH | d. | None of
the above |
|
|
|
3.
|
What is the driving force in the following reaction? Ni(NO 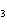 ) 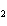 ( aq) 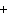 K 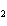 S( aq) 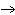 NiS (s) 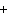 2KNO 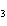 ( aq) a. | A gas is formed. | c. | Ionic compounds are reactants. | b. | A precipitate is
formed. | d. | Ionic compounds are
products. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Which compound dissociates to produce the ions Ca2+(aq) and
NO3–(aq)?
a. | CaNO3(s) | c. | Ca(NO3)2(s) | b. | Ca2NO3(s) | d. | Ca2(NO3)3(s) |
|
|
|
5.
|
If a combination/synthesis reaction takes place between rubidium and bromine,
the chemical formula for the product is ____.
a. | RuBr | b. | Rb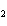 Br Br | c. | RbBr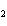 | d. | RbBr |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following is NOT a net ionic equation?
a. | Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq) ® AgCl(s) | b. | Fe2+(aq) +
2Cl–(aq) + 2OH–(aq) ®
Fe(OH)2(s) + 2Cl–(aq) | c. | 3Ca2+(aq) + 2P3–(aq) ® Ca3P2(s) | d. | Cu2+(aq) + S2–(aq) ® CuS(s) |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which compound dissociates to produce the ions
SO42–(aq) and NH4+(aq)?
a. | NH4SO4(s) | c. | NH4(SO4)2(s) | b. | (NH4)2SO4(s) | d. | (NH4)3(SO4)2(s) |
|
|
|
8.
|
A double-replacement reaction takes place when aqueous Na 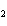 CO 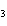 reacts with aqueous Sn(NO 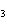 ) 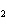 . You would expect one of the products of
this reaction to be ____.
|
|
|
9.
|
The equation 2C 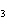 H 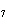 OH 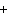 9O 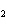  6CO 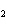 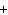 8H 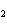 O is an example of which type of reaction? a. | combustion reaction | c. | double-replacement reaction | b. | single-replacement
reaction | d. | decomposition
reaction |
|
|
|
10.
|
Which of the following would form when Al(NO3)3(s)
dissolves in water ?
a. | Al+ + (NO3)3– | c. | Al3+ +
NO33– | b. | Al3+(aq) +
3NO3–(aq) | d. | Al3–(aq) +
3NO3+(aq) |
|
|
|
11.
|
When solutions of two ionic compounds are combined and a solid forms, the
process is called
a. | hydration. | c. | solvation. | b. | precipitation. | d. | dissociation. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following is a balanced equation representing the decomposition of
lead(IV) oxide?
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following pairs of solutions produce a precipitate when
combined?
a. | Cu(NO3)2 and NaCl | c. | Cu(NO3)2 and
K2CO3 | b. | Fe(NO3)3 and
MgCl2 | d. | CaCl2 and NaNO3 |
|
|
|
14.
|
The reaction 2Fe 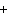 3Cl 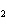 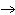 2FeCl 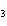 is an
example of which type of reaction? a. | combustion reaction | c. | combination/synthesis reaction | b. | single-replacement
reaction | d. | decomposition
reaction |
|
|
|
15.
|
What is the net ionic equation for the precipitation reaction between copper(II)
chloride and sodium hydroxide?
a. | Cu2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) ® Cu(OH)2(s) | b. | Na+(aq) + Cl–(aq) ® NaCl(s) | c. | Cu2+(aq) +
2OH–(aq) + 2Cl–(aq) ®
Cu(OH)2(s) + 2Cl–(aq) | d. | Cu2+(aq) + 2Cl–(aq) +
2Na+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) ®
Cu(OH)2(s) + 2NaCl(s) |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following dissociates in water?
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following would form when K2S(s) dissolves in
water?
a. | 2K+(aq) + S2–(aq) | c. | K2+(aq) + S2–(aq) | b. | K22+(aq) +
S2–(aq) | d. | 2K(aq) + S(aq) |
|
|
|
18.
|
What is the spectator ion in the equation
2Na+(aq) +
S2–(aq)+ Zn2+(aq) +
2NO3–(aq)® 2Na+(aq)+
2NO3-(aq) + ZnS(s)?
a. | ZnS(s) | b. | Na+(aq) | c. | S2–(aq) | d. | none of
these |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following statements is true about single-replacement
reactions?
a. | They are restricted to metals. | b. | They involve a single
product. | c. | One reactant switches places with another. | d. | Any metal replaces
any other metal. |
|
|
|
20.
|
In a double-replacement reaction, the ____.
a. | products are always carbon dioxide and water | b. | reactants are
usually two ionic compounds | c. | reactants are two elements | d. | products are a new
element and a new compound |
|
|
|
21.
|
A precipitation is an example of what type of reaction?
a. | composition | c. | single-replacement | b. | decomposition | d. | double-replacement |
|
|
|
22.
|
A double-replacement reaction takes place when aqueous cobalt(III) chloride
reacts with aqueous lithium hydroxide. One of the products of this reaction is ____.
a. | Co(OH)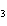 | b. | Co(OH)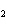 | c. | LiCo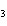 | d. | LiCl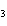 |
|
|
|
23.
|
In a combustion reaction, one of the reactants is always ____.
a. | hydrogen | b. | nitrogen | c. | oxygen | d. | a
metal |
|
|
|
24.
|
The type of reaction that takes place when one element reacts with a compound to
form a new compound and a different element is a ____.
a. | combination/synthesis reaction | c. | single-replacement
reaction | b. | decomposition reaction | d. | double-replacement reaction |
|
|
|
25.
|
What are the correct formulas and coefficients for the products of the following
acid/base (double replacement) reaction when the reaction is balanced? RbOH 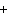
H 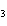 PO 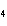 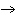
|
|
|
26.
|
The equation Mg( s) 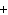 2HCl( aq) 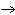 MgCl 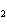 ( aq) 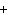 H 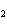 (g) (g) is an example of which type of
reaction? a. | combination reaction | c. | decomposition reaction | b. | single-replacement
reaction | d. | double-replacement
reaction |
|
|
|
27.
|
The equation H 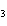 PO 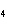 (aq)
(aq)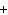 3KOH (aq)  K 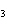 PO 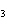 (aq) (aq)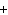 3H 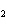 O (l) is an example of which
type of reaction? a. | double-replacement reaction | c. | decomposition
reaction | b. | combination reaction | d. | single-replacement reaction |
|
Matching
|
|
|
32-34 Match each equation with its correct type a. | acid-base reaction/double replacement | c. | precipitation reaction/double
replacement | b. | single replacement | d. | synthesis |
|
|
|
28.
|
Mg(s)  2HCl(aq) 2HCl(aq)  MgCl MgCl (aq) (aq) 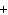 H H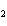 (g) (g)
|
|
|
29.
|
Ba(NO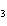 ) )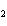 (aq) (aq) 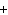 K K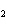 SO4(aq) SO4(aq) 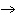 BaSO4(s)
BaSO4(s) 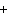 2KNO
2KNO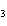 (aq) (aq)
|
|
|
30.
|
H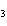 PO PO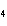 (aq)
(aq)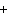 3KOH(aq) 3KOH(aq) 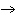 K K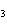 PO PO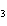 (aq) (aq)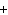 3H 3H O(l) O(l)
|
|
|
31.
|
2H2(g) + O2(g) 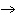 2H2O(g) 2H2O(g)
|
|
|
28 - 31 Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | combination/synthesis reaction | c. | combustion
reaction | b. | single-replacement reaction | d. | decomposition reaction |
|
|
|
32.
|
a reaction where one element switches places with the cation of the other
reactant
|
|
|
33.
|
a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler
substances
|
|
|
34.
|
a reaction in which 2 or more substances react to form one substance.
|
|
|
35.
|
a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat
or light
|