Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
If the pressure on the equilibrium system 2CO( g) +
O 2( g) 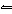 2CO 2( g) is increased, a. | the quantity of CO(g) increases. | b. | the quantity of
CO2(g) decreases. | c. | the quantity of CO2(g)
increases. | d. | the quantities in the system do not change. |
|
|
|
2.
|
Which symbol represents the equilibrium constant?
|
|
|
3.
|
If a reaction system has come to equilibrium, it can be made to run to
completion
a. | only if it is not reversible. | c. | by applying Le
Châtelier's principle. | b. | only if the temperature is low
enough. | d. | under no
circumstances. |
|
|
|
4.
|
At equilibrium,
a. | all reactions have ceased. | b. | only the forward reaction
continues. | c. | only the reverse reaction continues. | d. | both the forward and reverse reactions
continue. |
|
|
|
5.
|
At equilibrium, the total amount of the product(s)
a. | is always equal to the total amount of the reactants. | b. | is always greater
than the total amount of the reactants. | c. | is always less than the total amount of the
reactants. | d. | may be equal to, greater than, or less than the total amount of the
reactants. |
|
|
|
6.
|
A very low value of K indicates that
a. | equilibrium is reached slowly. | c. | reactants are
favored. | b. | products are favored. | d. | equilibrium has been reached. |
|
|
|
7.
|
A reaction in which products can react to re-form reactants is
a. | at equilibrium. | c. | buffered. | b. | reversible. | d. | impossible. |
|
|
|
8.
|
If the temperature increases on the following equilibrium system, what happens
to Keq?
2CH3OH (l) + 3O2 (g) + 1452 KJ
<==> 2CO2 (g) + 4H2O
(l)
a. | increases. | c. | increases or decreases. | b. | decreases. | d. | does not change. |
|
|
|
9.
|
How do coefficients from a chemical equilibrium appear when the chemical
equilibrium expression is written?
a. | as coefficients | c. | as subscripts | b. | as exponents | d. | they do not
appear. |
|
|
|
10.
|
What is the equilibrium constant, K, for the ionization of acetic acid,
shown in the reaction CH 3COOH( aq) + H 2O (l) 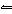 H 3O +( aq) +
CH 3COO –( aq)? a. | [H3O+]
[CH3COOH–] | c. | 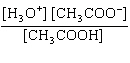
| b. | 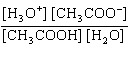 | d. | 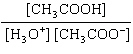 |
|
|
|
11.
|
In the equation 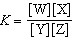 , what represents the concentrations of the
reactants? a. | [Y] and [Z] | c. | 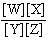 | b. | [W] and [X] | d. | 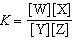 |
|
|
|
12.
|
An equilibrium mixture of SO 2, O 2, and SO 3
gases is determined to consist of 2 mol/L SO 2, 1
mol/L O 2, and 4 mol/L SO 3. What is the
equilibrium constant for the system at this temperature? The balanced equation for this reaction
is 2SO 2( g) + O 2( g) 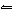
2SO 3( g).
|
|
|
13.
|
If the temperature of the equilibrium system CH 3OH( g) + 101 kJ
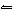 CO( g) + 2H 2( g) increases, a. | [CH3OH] increases and [CO]
decreases. | b. | [CH3OH] decreases and [CO]
increases. | c. | [CH3OH] increases and [CO]
increases. | d. | the concentrations in the system do not change. |
|
|
|
14.
|
What is the chemical equilibrium expression for the equation
2A 2B + 3CD 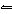 A 4D +
C 3B 2?
|
|
|
15.
|
A chemical reaction that includes only one state of matter is called
a. | heterogeneous | c. | homogeneous | b. | explosive | d. | none of these |
|
|
|
16.
|
Changing the pressure of a system mostly only affects
a. | solids | c. | gases | b. | liquids | d. | aqueous
solutions |
|
|
|
17.
|
Where would you find the activated comlex on a typical energy diagram?
a. | at the end with the products | c. | under the “hill”
| b. | at the beginning with the reactants | d. | at the top of the
“hill” |
|
|
|
18.
|
How much energy does the activated complex have compared to the rest of the
equation?
a. | less than the products | c. | more than both the reactants and products | b. | less than the
reactants | d. | ONLY more than
the reactants |
|
|
|
19.
|
What speeds up a reaction without being used up in the reaction?
a. | activation energy | c. | Keq | b. | catalyst | d. | collision model |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following does NOT affect reaction rates?
a. | particle size | c. | dynamic equilibrium | b. | concentration | d. | temperature |
|
|
|
21.
|
What is needed to cause molecules to brake apart when colliding?
a. | activation energy | c. | increase pressure | b. | dynamic equilibrium | d. | catalyst |
|
|
|
22.
|
The driving force behind chemical reactions taking place after compounds
“run in” to each other in order to break apart is called
a. | catalyst | c. | collision model | b. | reversible | d. | activation
energy |
|
Matching
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.
|
Represents the potential energy of the activated complex.
|
|
|
24.
|
Represents the potential energy of the reactants.
|
|
|
25.
|
Represents the activation energy of the forward reaction.
|
|
|
26.
|
Represents the activation energy of the reverse reaction.
|
|
|
27.
|
Represents the change in energy of the forward and reverse reaction.
|