Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. A | electronegativity | F | periodic law | B | ionization energy | G | cation | C | atomic
radius | H | period | D | metal | I | group | E | transition
metal | J | electrons |
|
|
|
1
|
horizontal row in the periodic table
|
|
|
2
|
vertical column in the periodic table
|
|
|
3
|
A repetition of properties occurs when elements are arranged in order of
increasing atomic number.
|
|
|
4
|
type of element that is a good conductor of heat and electric current
|
|
|
5
|
type of element characterized by the presence of electrons in the d
orbital
|
|
|
6
|
one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms when the atoms are
joined
|
|
|
7
|
type of ion formed by Group 2A elements
|
|
|
8
|
subatomic particles that are transferred to form positive and negative
ions
|
|
|
9
|
ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound
|
|
|
10
|
energy required to remove an electron from an atom
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
11
|
Which of the following electron box diagrams
correctly represents an atom of carbon?
|
|
|
12
|
Which of the following groups of atoms have the
same outermost electron configurations but with different (principal) energy
levels?
A | N, O, F, Ne | C | Ca, Ge,
Sr, In | B | S, Cl, Ar, K | D | O, S, Se,
Te |
|
|
|
13
|
Which of the following is NOT a valid electron
configuration?
A | 1s22s22p63s23p64s1
| C |
1s22s22p62d103s23p64s2
| B | 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d5
| D |
1s22s22p63s23p6 |
|
|
|
14
|
A student drew the following electron box diagram for an atom of sodium in the
ground state. 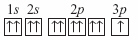 Which of the following statements is true? A | The student’s diagram is correct. | B | The student’s
diagram is incorrect because it shows an incorrect number of electron. | C | The student’s
diagram is incorrect because the arrows that represent the electrons should have opposite
spins. | D | The student’s diagram violates the law of conservation of
mass. |
|
|
|
15
|
For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited
state,
A | energy must be released. | B | energy must be absorbed. | C | radiation must be
emitted. | D | the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy
level. |
|
|
|
16
|
Bohr's theory helped explain why
A | electrons have negative charge. | B | most of the mass of the atom is in the
nucleus. | C | excited hydrogen gas gives off certain colors of light. | D | atoms combine to form
molecules. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
17
|
According to Bohr, electrons cannot reside at ____ in the figure above.
A | point A | C | point C | B | point B | D | point D |
|
|
|
18
|
A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best
represent
A | an s orbital. | C | a combination of px and py
orbitals. | B | a px orbital. | D | a combination of an s and a
px orbital. |
|
|
|
19
|
An orbital that could never exist according to the quantum or wave-mechanical
description of the atom is
|
|
|
20
|
The letter designations for the first four sublevels with the number of
electrons that can be accommodated in each sublevel are
A | s:1, p:3, d:10, and f:14. | C | s:2, p:6, d:10,
and f:14. | B | s:1, p:3, d:5, and f:7. | D | s:1, p:2, d:3, and
f:4. |
|
|
|
21
|
The number of orbitals for the d sublevel is
|
|
|
22
|
The atomic sublevel with the next highest energy after 4p is
|
|
|
23
|
If the s and p orbitals of the highest main energy level of an atom are filled
with electrons, the atom has a(n)
A | electron pair. | C | ellipsoid. | B | octet. | D | circle. |
|
|
|
24
|
The number of electrons in the highest energy level of the argon atom (atomic
number 18) is
|
|
|
25
|
In the Bohr model of the atom, an electron in an orbit has a fixed ____.
A | position | C | energy | B | color | D | size |
|
|
|
26
|
How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the
nucleus?
A | It decreases. | C | It stays the same. | B | It increases. | D | It doubles. |
|
|
|
27
|
What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital?
A | sphere | C | bar | B | dumbbell | D | two perpendicular
dumbbells |
|
|
|
28
|
The shape (not the size) of an electron cloud is determined by the
electron's ____.
A | energy sublevel (s, p, d, & f) | C | speed | B | diet | D | principal quantum number |
|
|
|
29
|
How are the frequency and wavelength of light related?
A | They are inversely proportional to each other. | B | Frequency equals
wavelength divided by the speed of light. | C | Wavelength is determined by dividing frequency
by the speed of light. | D | They are directly proportional to each
other. |
|
|
|
30
|
The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in
the sun would be ____.
A | the same | B | different from each other | C | the same as those of
several other elements | D | the same as each other only in the ultraviolet
range |
|
|
|
31
|
Which of the following electron configurations is most likely to result in an
element that is relatively inactive?
A | a half-filled energy sublevel | B | a filled energy sublevel | C | one empty and one
filled energy sublevel | D | a filled highest occupied principal energy
level |
|
|
|
32
|
Write the ground-state electron conguration of a
lead atom.
A | [Xe]
6s1 5d54f146p6 7s2 | C | [Xe] 6s1 5d10 4f14 6p3 | B | [Xe] 6s2
5d10 4f14 6p2 | D | [Xe]
6p4 4f14 5d10 |
|
|
|
33
|
Which of the following subshells CANNOT exist in an
atom?
|
|
|
34
|
In a given atom, how many electrons can occupy the
3d set of orbitals?
|
|
|
35
|
Which of the following is the correct orbital notation for the element oxygen
(O, atomic #8)?
|
|
|
36
|
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is the atom's
A | electron affinity. | C | electronegativity. | B | electron energy. | D | ionization
energy. |
|
|
|
37
|
The element that has the greatest electronegativity is
A | oxygen. | C | chlorine. | B | sodium. | D | fluorine. |
|
|
|
38
|
In a row/period in the periodic table, as you move across and as the atomic
number increases, the atomic radius generally
A | decreases. | C | increases. | B | remains constant. | D | becomes
unmeasurable. |
|
|
|
39
|
In the alkaline-earth group, atoms with the smallest radii
A | are the most reactive. | C | are all gases. | B | have the largest volume. | D | have the highest ionization
energies. |
|
|
|
40
|
As you move down the periodic table from carbon through lead, atomic
radii
A | generally increase. | C | do not change. | B | generally decrease. | D | vary
unpredictably. |
|
|
|
41
|
Electrons are elevated from the ground state to the excited state by:
A | the absorption of energy | C | the release of
energy | B | the loss of mass | D | the destruction of energy |
|
|
|
42
|
When a salt such as sodium chloride is exposed to a flame, the visible light
given off is the result of:
A | ground state electrons moving to higher energy levels | C | excited electrons returning to the
ground state | B | nuclear decay | D | gamma radiation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
43
|
Given the representation of a chlorine atom, which circle might be a chloride
ion, Cl-?
A | Circle D | C | Circle B | B | Circle C | D | None of these |
|
|
|
44
|
Cations have a ______________ charge and are ______________ than the atoms from
which they formed.
A | positive/larger | C | negative/larger | B | negative/smaller | D | positive/smaller |
|
|
|
45
|
What element has the noble-gas notation
[Ne]3s23p5?
A | Chlorine | C | Sulfur | B | Neon | D | Oxygen |
|
|
|
46
|
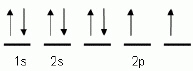 The "up" and "down" arrows
in electron orbital notation, such as is shown here, depict: A | electrons and protons attracting each other | C | protons and neutrons in
orbitals | B | oppositely charged electrons | D | electrons with opposite spins |
|
|
|
47
|
The elements on the modern periodic table are organized by increasing:
A | atomic number | C | ionization energy | B | atomic mass | D | size |
|
|
|
48
|
The elements of the Noble Gas family, except for Helium, have an outer shell of:
A | 6 electrons | C | 2 electrons | B | 8 electrons | D | 18 electrons |
|
|
|
49
|
Which element is predicted to have the ground-state
electron conguration [He] 2s2?
A | beryllium | C |
boron | B | lithium | D | carbon |
|