Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Carbon shows a very strong tendency to form
a. | ionic bonds. | c. | hydrogen bonds. | b. | covalent bonds. | d. | highly polar
bonds. |
|
|
|
2.
|
How many covalent bonds can a carbon atom usually form?
|
|
|
3.
|
What do all organic compounds contain?
a. | hydrogen | c. | oxygen | b. | water | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
4.
|
Organic compounds are so numerous because carbon atoms
a. | are highly electronegative. | c. | are very small. | b. | can bond with each
other in many ways. | d. | are
stable and very common in nature. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms are connected by only single bonds in
straight chains or branched chains are called
a. | aromatic hydrocarbons. | c. | alkenes. | b. | alkynes. | d. | alkanes. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Hydrocarbons in which carbon atoms form only single bonds and are arranged in a
ring are called
a. | cycloalkanes. | c. | alkenes. | b. | alkynes. | d. | aromatic
hydrocarbons. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.
|
In the figure above, name the compound in diagram D.
a. | 2-bromopropyne | c. | 2-bromopropane | b. | 2-bromopropene | d. | 2,2-bromopropene |
|
|
|
8.
|
In the figure above, name the compound in diagram A.
a. | ethane | c. | ethyne | b. | ethene | d. | ethadiene |
|
|
|
9.
|
In the figure above, name the compound in diagram C.
a. | diethylpentane | c. | 3-methylpentane | b. | 3-isoheptane | d. | 3-ethylpentane |
|
|
|
10.
|
In the figure above, name the compound in diagram B.
a. | 1,3-butadiene | c. | 2,3-butadiene | b. | 1,4-butadiene | d. | 1,3-butene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.
|
In the figure above, which structural formula represents
methylcyclohexane?
|
|
|
12.
|
In the figure above, name the compound in diagram B.
a. | 1,1-dimethylcyclopentane | c. | cycloheptane | b. | ethylcyclopentane | d. | propylcyclohexane |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which hydrocarbons are saturated?
a. | alkenes | c. | alkynes | b. | alkanes | d. | aromatic
hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
14.
|
The two resonance structures of benzene have
a. | only single bonds. | c. | alternating double and triple bonds. | b. | only double
bonds. | d. | alternating single
and double bonds. |
|
|
|
15.
|
How many double covalent bonds are in an alkane?
|
|
|
16.
|
How many carbons are in a molecule of hexane?
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is a condensed structural formula for propane?
|
|
|
18.
|
The name for an alkyl group that contains two carbon atoms is ____.
a. | diphenyl | c. | dimethyl | b. | ethyl | d. | propyl |
|
|
|
19.
|
What is the name of the compound CH 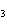 CH(CH 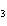 )C(CH 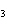 ) 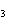 ? a. | 2,2,3-trimethylbutane | c. | 1,1,1,2-tetramethylpropane | b. | tetramethylpropane | d. | isoheptane |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of the following compounds is an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
a. | methane | c. | nonane | b. | propyne | d. | methyl |
|
|
|
21.
|
The general name for hydrocarbons with at least one triple covalent bond is
____.
a. | alkenes | c. | alkanes | b. | alkyls | d. | alkynes |
|
|
|
22.
|
What is the name of the smallest alkyne?
a. | butyne | c. | methyne | b. | ethyne | d. | propyne |
|
|
|
23.
|
The most important way to classify organic compounds is by ____.
a. | the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain | b. | functional
group | c. | the type of carbon—carbon bonds | d. | reactivity |
|
|
|
24.
|
What type of compound is CH 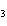 ¾ ¾O ¾CH 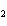 ¾ ¾CH 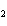 ¾ ¾CH 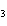 ? a. | alcohol | c. | ether | b. | aldehyde | d. | ketone |
|
|
|
25.
|
Name the following compound. CH 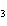 ¾ ¾CH 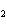 ¾ ¾CH 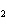 ¾ ¾CH 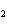 ¾ ¾O ¾CH 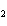 ¾ ¾CH 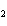 ¾ ¾CH 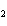 ¾ ¾CH 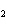 ¾ ¾CH 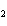 ¾ ¾CH 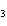 a. | butoxyhexane | c. | hexylbutane | b. | butylcyclohexyl | d. | butylhexane |
|
|
|
26.
|
Name the compound CH 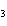 CH 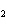 O CH 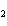 CH 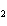 CH 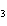 . a. | diethyl propane | c. | ethoxypropane | b. | dipropyloxyether | d. | pentoxy ether |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which carbon skeleton represents an ether?
a. |
C¾C¾C¾O¾C¾C¾C | c. |
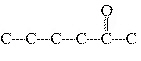 | b. |
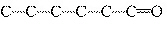 | d. |
none of the
above |
|
|
|
28.
|
A ketone has the general structure ____________.
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.
|
In the figure above, what is the structural formula for butane?
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.
|
In the figure above, what is the structural formula for propyne?
|
|
|
31.
|
Which hydrocarbons do NOT have double or triple bonds?
a. | alkanes | c. | alkynes | b. | alkenes | d. | alkadienes |
|