Multiple Choice
Identify the
letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Who first recognized that the ratio of the number of atoms that combine is the
same as the ratio of the masses that combine?
a. | Jons Berzelius | c. | John Dalton | b. | Edward Morley | d. | Jon Newlands |
|
|
|
2.
|
Because most particles fired at metal foil passed straight through, Rutherford
concluded that
a. | atoms were mostly empty space. | c. | electrons formed the
nucleus. | b. | atoms contained no charged particles. | d. | atoms were
indivisible. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Rutherford fired positively charged particles at metal foil and concluded that
most of the mass of an atom was
a. | in the electrons. | c. | evenly spread throughout the atom. | b. | concentrated in the
nucleus. | d. | in rings around
the atom. |
|
|
|
4.
|
The mass of a neutron is
a. | about the same as that of a proton. | c. | double that of a
proton. | b. | about the same as that of an electron. | d. | double that of an
electron. |
|
|
|
5.
|
The nucleus of most atoms is composed of
a. | tightly packed protons. | c. | tightly packed protons and
neutrons. | b. | tightly packed neutrons. | d. | loosely connected protons and electrons. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Protons have
a. | negative charges. | c. | no charges. | b. | an attraction for neutrons. | d. | no mass. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The charge on the electron cloud
a. | prevents compounds from forming. | b. | balances the charge on the
nucleus. | c. | attracts electron clouds in other atoms to form compounds. | d. | does not
exist. |
|
|
|
8.
|
The smallest unit of an element that can exist either alone or in combination
with other such particles of the same or different elements is the
a. | electron. | c. | neutron. | b. | proton. | d. | atom. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Atoms of the same element that have different masses are called
a. | moles. | c. | nuclides. | b. | isotopes. | d. | neutrons. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Isotopes of an element contain different numbers of
a. | electrons. | c. | neutrons. | b. | protons. | d. | nuclides. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is its
a. | atomic number. | c. | mass number. | b. | Avogadro constant. | d. | number of
neutrons. |
|
|
|
12.
|
As the mass number of the isotopes of an element increases, the number of
protons
a. | decreases. | b. | increases. | c. | remains the
same. | d. | doubles each time the mass number increases. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The average atomic mass of an element depends on both the masses of its isotopes
and each isotope's
a. | atomic number. | c. | relative abundance. | b. | radioactivity. | d. | mass number. |
|
|
|
14.
|
What is the atomic number for aluminum?
|
|
|
15.
|
A neutral atom of silicon contains___________ .
a. | 14 electrons. | c. | 16 electrons. | b. | 28.09 electrons. | d. | 38 electrons. |
|
|
|
16.
|
An atom of potassium has 19 protons and 20 neutrons. What is its mass
number?
|
|
|
17.
|
Ag-109 has 62 neutrons. The neutral atom has
a. | 40 electrons. | c. | 53 electrons. | b. | 47 electrons. | d. | 62 electrons. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Carbon-14 (atomic number 6), the radioactive nuclide used in dating fossils,
has
a. | 6 neutrons. | c. | 10 neutrons. | b. | 8 neutrons. | d. | 14 neutrons. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Silicon-30 contains 14 protons. It also contains
a. | 16 electrons. | c. | 30 neutrons. | b. | 16 neutrons. | d. | 44 neutrons. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Mendeleev's table was called periodic because the properties of the
elements
a. | showed no pattern. | b. | occurred at repeated intervals called
periods. | c. | occurred at regular time intervals called periods. | d. | were
identical. |
|
|
|
21.
|
What are the elements with atomic numbers from 58 to 71 in the periodic table
called?
a. | the lanthanide elements | c. | the actinide
elements | b. | the noble gases | d. | the alkali metals |
|
|
|
22.
|
Argon, krypton, and xenon are
a. | alkaline earth metals. | c. | actinides. | b. | noble gases. | d. | lanthanides. |
|
|
|
23.
|
In the modern periodic table, elements are ordered according to
a. | decreasing atomic mass. | c. | increasing atomic
number. | b. | Mendeleev's original design. | d. | the date of their
discovery. |
|
|
|
24.
|
To which group do lithium and potassium belong? Refer to your periodic
table.
a. | alkali metals | c. | halogens | b. | transition metals | d. | noble gases |
|
|
|
25.
|
Refer to your periodic table. To which group do fluorine and chlorine
belong?
a. | alkaline-earth metals | c. | halogens | b. | transition elements | d. | actinides |
|
|
|
26.
|
What does the number 84 in the name krypton-84 represent?
a. | the atomic number | c. | the sum of the protons and electrons | b. | the mass
number | d. | twice the number of
protons |
|
|
|
27.
|
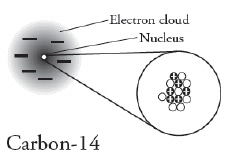 How many neutrons are found in this
isotope of Carbon?
|
|
|
28.
|
Two isotopes of a new element, Dontpanicium (Dpg), was discovered in the back
hills of Whittier. One isotope had a mass of 255 and the other as mass of 261. Dpg-255
has a relative abundance of 35% and Dpg-261 has a relative abundance of 65%. What is the
average atomic mass of Dpg?
a. | 256.9 | c. | 258.9 | b. | 257.9 | d. | 259.9 |
|
|
|
29.
|
The following data was collected from a student’s Isotopes of Pennium
Lab. Number of Pre-‘82 Pennies (relative
abundance) | 12
(60%) | Number of Post-‘82 Pennies (relative abundance) | 8 (40%) | Ave. Atomic Mass of Pre-‘82 Pennies | 3.00 | Ave. Atomic Mass of Post-‘82 Pennies | 2.50 | | |
Calculate the Ave. Atomic Mass of this sample
of Pennium using the following equation: Ave. Atomic Mass of Pe = (relative abundance of
pre-‘82 pennies x Ave. At. Mass Pre-‘82 Pennies) + (relative abundance of
post-‘82 pennies x Ave. At. Mass of post-‘82 pennies)
|
|
|
30.
|
Two isotopes of a new element (Ma) recovered from Mars have mass numbers of 130
and 132. Ma-130 has a relative abundance of 20% while Ma-132 has a relative abundance of 80%. What is
the Average Atomic Mass of Ma?
a. | 130.6 | c. | 131.6 | b. | 129.6 | d. | 132.6 |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | proton | d. | electron | b. | nucleus | e. | neutron | c. | atom |
|
|
|
31.
|
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that
element
|
|
|
32.
|
a positively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
33.
|
a negatively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
34.
|
a subatomic particle with no charge
|
|
|
35.
|
the central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons
|